Table of Contents
Instrumentation Cable | Instrument Cable
In numerous industrial and processing tasks, an instrumentation cable is essential. Without this wire, it is challenging to monitor and manage power systems and the supporting operations. It emits low-energy signals that can be used to control or monitor a number of important electronic circuit-dependent processes.
Signal broadcasts have been made simpler by modern wireless transmission technologies. The wireless transmission and reception of information is commonplace. Because wireless transmissions are becoming popular, the majority of us lack substantial understanding about shielded instrument cable. The relevance of this cable, which transfers messages in electric circuits, can be seen in a number of different businesses, such as; the sector of petrochemicals, Fertilizer plants Cement manufacturing facilities, steel businesses.
What is an Instrument Cable ?
A form of wire with numerous conductors called an instrumentation cable is used to send low-energy electric signals. Cables and electrical wires carry out a range of functions in a number of industrial applications. For example, they could convey electrical power, data, or communications. A cable is normally constructed in accordance with the application for which it is intended and includes a variety of protective components.
These cable types were developed by manufacturers of instrumentation cables to offer adequate shielding against any kind of outside signal interference. Their main responsibility is to monitor and manage various electric systems and related operations. In essence, they contribute to the smooth running of numerous industrial processes. Also crucial to keep in mind is how frequently these cable types are employed in instrumented systems that contain computers and grounded microprocessors. Because they are resistant to interruptions and interference from outside sources, these cables are useful in numerous control and communication applications. They are useful for voice transmissions, signal relays, analogue or digital signal processing, process regulation, and control circuitry. Due to the nature of its applications, a flexible instrumentation cable would be the best choice. If you need a signal transmission cable for the process, petrochemical, fertiliser, or steel industries, this is the one to choose.
What are the types of Instrumentation cable | Types of instrument cables
Instrumentation cables often have a wide range of applications. They have excellent electrical, thermal, and physical characteristics and are designed for severe conditions. According to the type of insulation and the method of shielding, they are available in various assortments. An extensive list of the various types of instrumentation cables is provided below. so Instrumentation cables comes in following types.
1. PVC Instrument Cable
This cable variant has an exterior covering made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as the name would imply. Due to its exceptional qualities, PVC is undoubtedly the most widely used thermoplastic insulating material. The substance naturally resists moisture, fire, and all types of scrapes. Copper, which is renowned for having excellent electrical conductivity, serves as the conductor material for the cable. It also complies with a number of major cable building standards, such as BS-EN-50288, UL 2250, EIL 6-52-46, etc. PVC instrument cable is one of the major cables used in the industry.
2. XLPE Instrument Cable
The highest quality cross-linked polyethene material is used in the construction of the XLPE instrumentation cable. Strong molecular three-dimensional bond structures can be found in this sort of insulation material. The wire is resistant to UV radiation, grease, and all other types of environmental challenges. The cable is made of extremely flexible stranded copper conductors for optimal electrical conductivity, just as the PVC instrumentation cable.
No matter what kind of instrumentation cable you choose. You must keep in mind that there are several forms of shielding. For this kind of cable, the shielding options are;
(I). Overall Shielded Pair/Triad Instrument cable
Cables that have been twisted together and encased in a shield, such as foil or mesh, are known as overall shielded pair cables. These shields guard against electromagnetic interference on the wires. The majority of crosstalk may be effectively eliminated via shielded cables. Shielded cables do need a ground, which is another important distinction between shielded and unshielded cables. Although their installation may need for a little more skill, they offer great data transfer rates.
(II). Individual Shielded Pair/Triad Instrument cable
Cable that have individual pair/ triad encased in shield know as individual shielded pair/triad instrument cable. Analog signals are normally sent using the individually shielded pair architecture, whereas digital signals are typically transmitted using the overall shielded pair cables.
3. Armoured Instrument cable
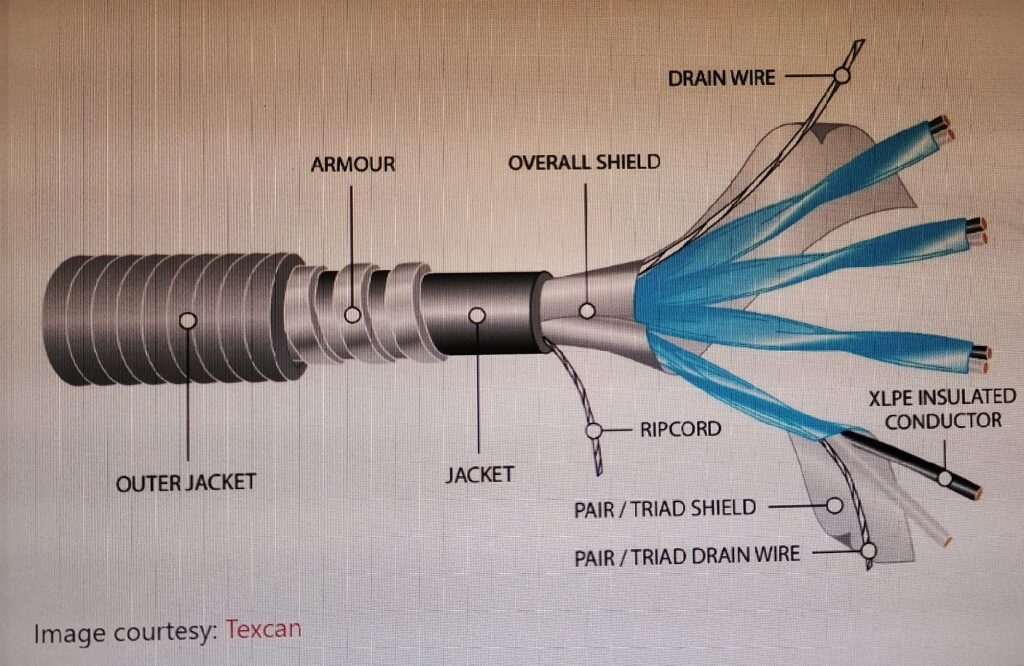
By avoiding crosstalk between pairs and triads, armoured instrumentation cables can be utilised to limit noise and signal interference. Signal conversion for analogue or digital signals is also possible with this cable. The cable’s armour guards it against physical harm, mechanical pressure, and other vibration shocks. Steel wire armoured (SWA), steel wire braided (SWB), and steel tape armoured(STA) are the three main types of armour. An aluminium or steel wire armoured cable’s construction typically consists of following parts:
1. Plain stranded copper or aluminium conductor.
2. Insulation: Materials like cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) offer good dielectric strength and high temperature tolerance, resulting in improved electrical qualities.
3.Bedding: A covering to act as a barrier between the armour and the insulation.
4. Armor: An armour made of steel or aluminium offers mechanical protection, enabling the cable to endure the mechanical pressures to which it is subjected.
5.Sheath: The cable’s component pieces are linked together by a sheath that provides an additional layer of protection. For UV stability, black sheaths might be filled with carbon.
6. Drain wire: It is tinned copper. To achieve efficient grounding, drain wires and a metallic shield are utilised in cables. The drain wire completes an electrical circuit from the shield and transports unwelcome electrical interference to ground.
7.Shielded Twisted Pair: A foil shield made of 100% aluminium and polyester with a separate drain wire.
8.Overall Shielded: 100% coverage aluminum/polyester foil shield with a separate drain wire.
9.Rip Cord: For easy removal, rip the cord underneath the jacket.
10.Outer and inner jacket: Black Polyvinyl Chloride that is moisture- and sunlight-resistant (PVC)
4. Single pair and multi pair instrument cables
Single-pair, multi-pair, and triple cables are the most common forms of instrumentation cables used to transmit electrical signals between various instruments, controllers, PLCs, DCS, etc.
The effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) from outside sources are lessened by twisting the single-pair or multi-pair cables. These aid in minimising crosstalk between adjacent pair cables.
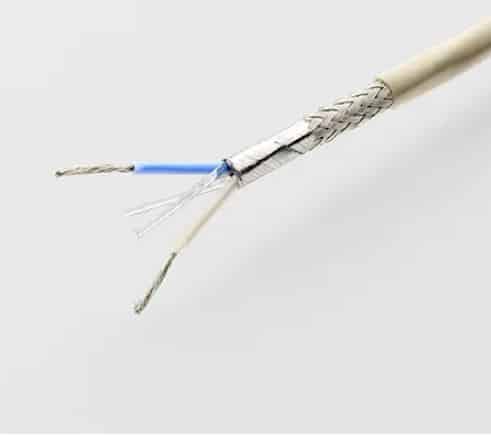










- multi pair instrumentation cable
For analogue signals, the individually shielded pair construction is commonly employed, while for digital signals, the construction with entire shield only.
The three wire RTDs and corresponding transmitters are also connected using triad cables. Triad cables are sometimes used to connect temperature scanners and RTDs installed on high-capacity motors.
Control cable vs Instrument cable
An instrumentation-type cable and a control cable are often mistaken for one another, especially by persons who are unfamiliar with electrical cables. Because control wires are a member of the instrumentation cable family, confusion about them frequently occurs. It’s important to keep in mind that these two cables differ significantly in some key ways. The primary distinction between these cables is based on how they are used. Control cables are often useful in circumstances where larger wires capable of withstanding extremely high electrical currents are required. Smaller diameter and stranded conductors in instrumentation-type cables ensure maximum flexibility. Consequently, if you want to carry out wiring tasks that demand the greatest amount of flexibility, it is best. In addition, instrumentation cables contain shields to prevent electromagnetic interference from affecting their performance. Foil-type shielding and braid-type shielding are typically the two types of shielding that cable manufacturers employ. A shielded instrumentation cable is essential for all instrumentation applications, in contrast to a control cable whose circuit does not call for shielding.
Speaker cable vs instrument cable
Speaker and instrument cables are built very similarly. With connectors made of gold, nickel, or other metals, they have a copper core that is encased in rubber or polyester. Speaker cables are unshielded and use big wire gauges, whereas instrument cables are protected and use much smaller wires.
A speaker wire doesn’t need shielding because the amp’s signal is very strong and the speaker’s impedance is so low that outside interference and RF noise won’t be an issue. In contrast, an instrument cable needs shielding because it links your instrument to the amplifier at a high impedance. Because the signal line is protected, radio waves and electrical interference are diminished.
Instrument cable features
Instrumentation cable should have following features.
Really light.
Secure and protected.
Efficient and dependable.
Chloroprene cables are light and portable.
Circuit implementation is simple.
Instrumentation Cable can be applied to dry, moist, or wet environments.
Low voltage data and signals are frequently distributed.
Up to 40 volts of signal voltage can be carried by these instrumentation cables.
Instrumentation cables can be used to transmit electrical signals in industrial control circuits and electrical installation.
For the most demanding applications, there are several conductors, filters, and jacket materials available.
Options for jacket materials that offer high flexibility and superior mechanical protection.
made with stripping and overmolding in mind.
selection of instrument cable dimensions.
Screening alternatives include aluminium foil with drainwire, bare copper braid, braid with drainwire, and optimised braids with superior surface transfer impedance properties.
Instrumentation cable application
Following are the application and uses of instrument cables
Cable for instrumentation in steel mills
EOT crane instrumentation and signal cable.
Instrumentation cable for airport lighting rated at 300/500V IS/OS.
Cables for ship instrumentation and control.
Instrumentation Cable with PE Insulation for Nuclear and Thermal Power Plants
EN 50288-7 Instrumentation Cable For wind power mills, use 1pr 3pr 6pr x 16awg.
Copper instrumentation cable for electrical machines with a 300V PVC insulation.
Textile machine instrumentation and signal cables.
Instrumentation cable for turbines that is 300/500V IS/OS is available for construction equipment. These are the some application and uses of instrument cables.
Faqs
bulk instrument cable
You must first comprehend what is intended by a bulk cable and internet contract. Simply put, this is a deal between a HOA or condominium association and a provider of cable and internet services for each and every community resident.
Instrument cable manufacturer
There are lots of manufacturer who manufacture instrument cable. some of them are given below.
- AEG (NEXANS FRANCE)– France
- BICC(PIRELLI INDUSTRIAL CABLES LIMITED)-UK
- BV.TWENTSCHE KABELFABRIEK (TKF)- Netherlands
- CAVICEL, SPA- Italy
- DAEWON CABLE CO.,LTD-Korea
- FUJI KURA(FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD- Japan
- FURUKAWA- Japan
- HITACHI- Japan
- KERPENWERK(KERPEN GMBH & CO.)_-Germany
- PIRELLI CAVI E SISTEMI S.P.A.- Italy
- RAMCRO S.P.A- Italy
- SIEMENS-Germany
- SUMITOMO-japan
custom instrument cables
Cable which are manufacture on demand of client or customize as per clients requirement are called “custom instrument cable”
mogami instrument cables
The most reputable cable for bass guitar, keyboards, pedals, and guitars of all kinds is made by Mogami. Additionally, Mogami manufactures cables for powered speakers, DJ equipment, headphones, iPod®/MP3 players, and microphones for studio and live performances.
monster instrument cable
High-quality cables for connecting audio and video devices are produced by the Californian company Monster Cable. Blu-ray players, stereo receivers, and speaker systems are some examples of this gear.
gpib cable national instruments
General Purpose Interface Bus, or GPIB, was created as a bridge between computers and measurement devices. PCs and measurement devices are mostly connected via it.
Recommended artcicles
What is rectifier ? | Types and Circuit diagram.
Laser Sensor | What is laser Sensor?
What is mean by “Control” in Instrumentation