Table of Contents
“Transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form for the purpose of measurement and control.” Most of the transducers are based on converting physical quantities such as pressure, force, temperature, liquid level, fluid flow etc. into a measurable or detectable change for measurement and control the particular physical variable.
A block diagram is shown below to understand as follows–
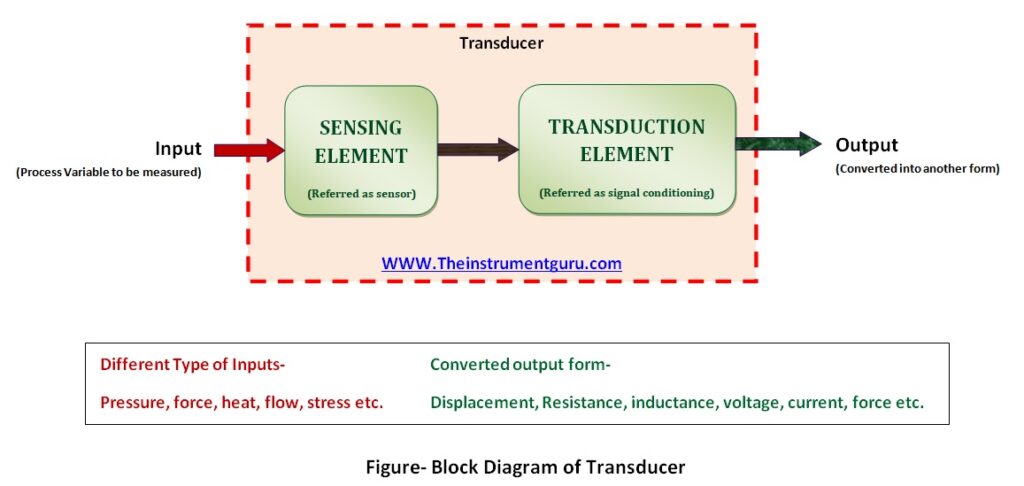
Referring to the block diagram, it is clear that a transducer is a combination of a sensing element also known as a primary sensing element or a sensor and a transduction element that provide signal conditioning for the sensor output.
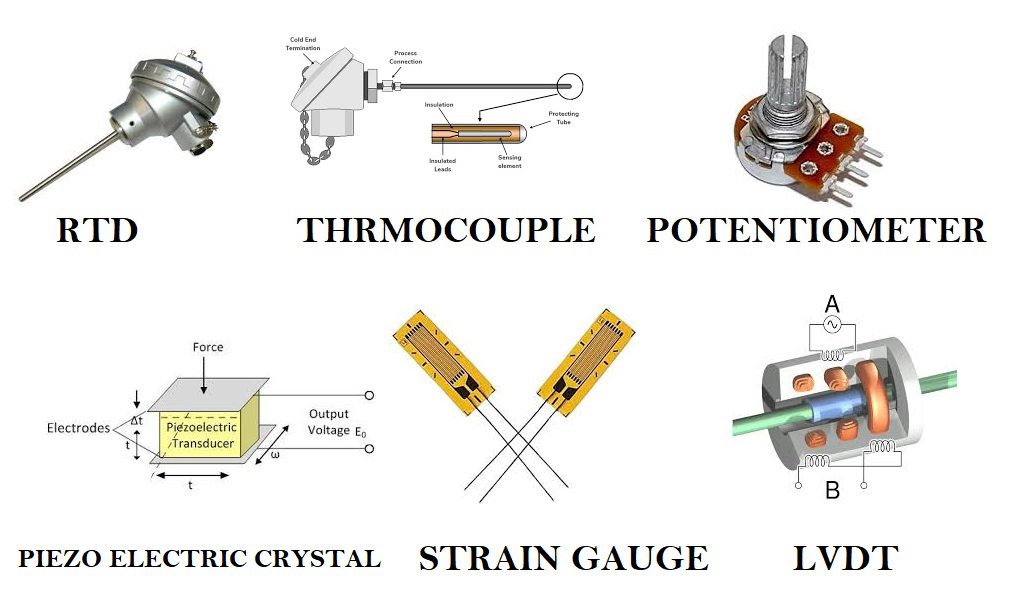
Transducer Examples
Some examples of transducers are as follows-
- Thermistor– temperature change is converted into output resistance
- Potentiometer– Displacement change is converted into output resistance
- Thermocouple– temperature is measured by detecting thermo EMF between two dissimilar metal junctions.
- I to P converter– Converts current signal (4-20)mA into proportional pressure signal (3-15)PSI
- P to I Converter– Converts pressure signal into proportional current output
- Piezo-Electric Crystal– uses property of certain materials to generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress and vice versa
- Strain Gauge– converts force, pressure, tension, weight, etc., into a change in electrical resistance
- LVDT- convert change in small displacement into electrical output
- RTD- temperature change is converted into output resistance




Characteristics of Transducer
Characteristics of transducer are defined as a list of parameters which determines static and dynamic characteristics that helps during selection of a right transducer converting a physical process variable into suitable output result for the purpose of measurement and control. Its characteristics and selection parameters both the topics will be discussed here. There are various characteristics as shown as follows-
- Accuracy
- Ruggedness
- Linearity
- Repeatability
- Sensitivity
- Resolution
- Stability and reliability
- Dynamic range
- Transducer size
- Speed of response etc.
Transducer selection Criteria
- Operating principle under which transducer working principle is based should be selected and depend upon nature and properties of the process variable to be measured. The operating principle of it may be resistive, inductive, capacitive, optical etc.
- Operating range & maximum sustaining range should be selected appropriately for the measurement of process variable to achieve good resolution and to determine maximum operating condition such as pressure, temperature etc.
- The accuracy should be as high as possible or as per the measurement.
- They should be more sensitive to produce the higher output change with respect to a small change in input process variable or sensitivity should be as per requirement.
- Their input impedance should be high and output impedance should be low to avoid loading effect.
- The error produced by the it should be low as possible.
- They should maintain input and output characteristic for the selected environmental condition.
Read Also:-
Electrical Transducer
Related Search:-




How to choose zener diode barriers?
How to choose zener diode barriers?




How Infra Red(IR) Gas analyzer Work
How Infra Red(IR) Gas analyzer Work





What is pressure switch?
What is pressure switch?





Valve Positioner
Valve Positioner




How to Measure Conductivity?
How to Measure Conductivity?




