Table of Contents
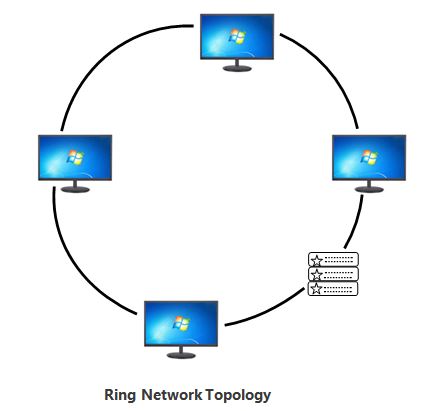
Ring Network Topology: With the exception of connected ends, ring network topology is similar to bus topology. This type of topology is usually divided into two types: unidirectional and bidirectional. A unidirectional ring network allows packets to go only in one way, but a bidirectional ring network allows data to move in any direction. Every device can be connected using two devices to construct a circular lane in this architecture. A token of this type topology is one in which data is transmitted from one device to another until it reaches its destination using tokens. As a result, when we connect different computers as well as other network nodes in a ring topology configuration, the computer network is referred to as a ring network. When this topology with a large number of nodes is employed, a number of repeaters are necessary because if someone wishes to send data to the last node in this topology with 100 nodes, the data must pass through 99 nodes before reaching the 100th node. As a result, repeaters are utilised in the network to prevent data loss.
The transmission is unidirectional, but it may be made bidirectional by connecting each Network Node with two connections, which is known as Dual Ring Topology.
Ring topology diagram:
Diagram is as below.
Applications of Ring network Topology:
The following are some of the applications of this topology.
A LAN (local area network) and a WAN (wide area network) both use this network structure (Wide area network).
In the sphere of communications, this type of architecture is employed in Synchronous optical network (SONET) fibre.
Because of its cheap operating costs, it can also be used in educational institutions.
Read Also
Examples of Ring Topology:
this type of topology is primarily utilised in two types of networks: local area networks (LAN) and wide area networks (WAN). As the signal goes across all computers, data packages travel in a unidirectional manner from one device to the next.
The data is delivered from one device to another in the small machine network in colleges, where campus computers are linked in nodes.
The SONET network is used to carry a large number of phone calls and data through a unidirectional optical fibre channel.
Advantages and disadvantages:
The following are some of the advantages and disadvantages of Dual Ring topology.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
When data is transmitted, packets move along the circle, passing through each of the intermediary nodes until they reach their destination, because each device is only connected to the ones on either side. Repeaters can be used to ensure packets arrive accurately and without data loss when a big network is set up in a this type topology.
Ring topologies are efficient in transmitting data without errors because only one station on the network can send data at a time, drastically reducing the likelihood of packet collisions.
Ring topologies are generally cost-effective and straightforward to set up, and the complex point-to-point connectivity of the nodes makes it reasonably easy to spot network problems or misconfigurations.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
Despite its popularity, this topology is nevertheless vulnerable to failure if it is not properly managed. Because data transmission is unidirectional between nodes along each ring, if one goes down, the entire network falls down with it. As a result, it’s critical that each of the nodes be monitored and kept in good working order. Even if you’re alert and attentive to node performance, a transmission line failure might bring your network to a halt.
The issue of scalability should be taken into account as well. Because all of the devices on the network share bandwidth in a ring architecture, adding more devices can cause overall communication delays. To avoid overburdening the network’s resources and capacity, network managers must be cautious of the devices introduced to the topology.
In order to reconfigure, add, or delete nodes, the entire network must be taken offline. While this isn’t the end of the world, it can be difficult and costly to schedule network downtime.
The transmission is unidirectional, but it may be made bidirectional by connecting each Network Node with two connections, which is known as Dual Ring Topology.
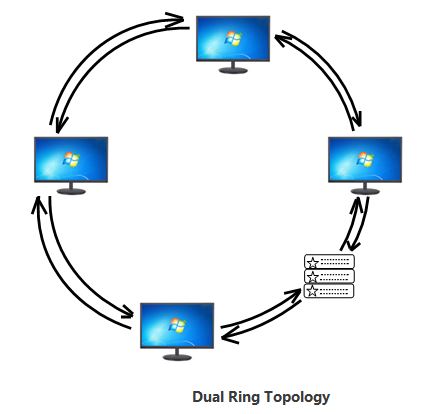
Dual-Ring Topology:
A ring topology network is half-duplex, which means data can only flow in one way at a time. A dual ring topology can be created by adding a second connection between network nodes to make ring topologies full-duplex.
Dual Ring topology diagram:
Dual Ring Topology Diagram is as below.




Dual Ring topology advantages and disadvantages:
The following are some of the advantages and disadvantages .
Benefits
Because each node has two connections on either side, information may be transferred both clockwise and counterclockwise along the network. In a dual-ring topology configuration, the secondary ring can operate as a redundant layer and backup, alleviating many of the drawbacks of standard ring architecture. Dual ring topologies also add a layer of security: if one ring within a node fails, the other ring can continue transfer data.
Disadvantage
In this topology, troubleshooting is challenging.
The addition of stations between them or the removal of stations can cause the entire topology to be disrupted.
It’s less safe.
Read Also