Table of Contents
NDT full form of Non destructive testing, commonly referred to as NDT, is a technique used to evaluate materials, components, and systems without causing damage to them. This is done by inspecting the object for flaws or irregularities that may affect its structural integrity or performance. NDT is an important part of many industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and manufacturing. It is used to ensure the quality and safety of products, to detect defects and prevent failures, and to reduce the need for costly and time-consuming repairs or replacements. NDT, or Non-Destructive Testing, is a set of techniques used to inspect and evaluate the properties of materials and structures without damaging them. The principle of NDT is based on the fact that materials and structures exhibit characteristic responses to different types of stimuli, such as heat, sound, light, or magnetic fields. These responses can be measured and analyzed to infer the internal condition of the material or structure being tested. NDT is to ensure that the testing is performed by qualified and experienced personnel who have the knowledge and skills necessary to interpret the test results correctly. NDT technicians must follow established procedures and standards to ensure that the testing is performed safely, accurately, and reliably.

Types of NDT :-
NDT stands for Non-Destructive Testing, which is a group of analysis techniques used to evaluate the properties and conditions of materials, components, and systems without causing damage to them. There are many different types of NDT methods, and some of the most common ones include:
1-Visual inspection
This is the most basic form of NDT and involves simply looking at an object for defects. It is often used as a first step in the inspection process to identify any obvious flaws. Visual inspection is one of the most common and widely used methods of non-destructive testing (NDT). It involves a thorough visual examination of the surface and interior of a material or structure to detect any visible signs of damage, wear, or defects. During a visual inspection, a trained inspector examines the material or structure for any visible signs of cracks, corrosion, deformation, discoloration, or other abnormalities. The inspector may use various tools such as a flashlight, magnifying glass, or borescope to help identify defects in hard-to-reach areas. Visual inspection can be performed on a wide range of materials and structures, including metals, plastics, ceramics, composites, concrete, and wood. It is often used as a first-line screening tool to identify potential defects or areas of concern before more advanced NDT methods are employed. Visual inspection is a relatively low-cost and simple technique, and it does not require specialized equipment or extensive training. However, the effectiveness of visual inspection depends on the skill and experience of the inspector, as well as the quality of the lighting and viewing conditions.




2-Radiographic testing
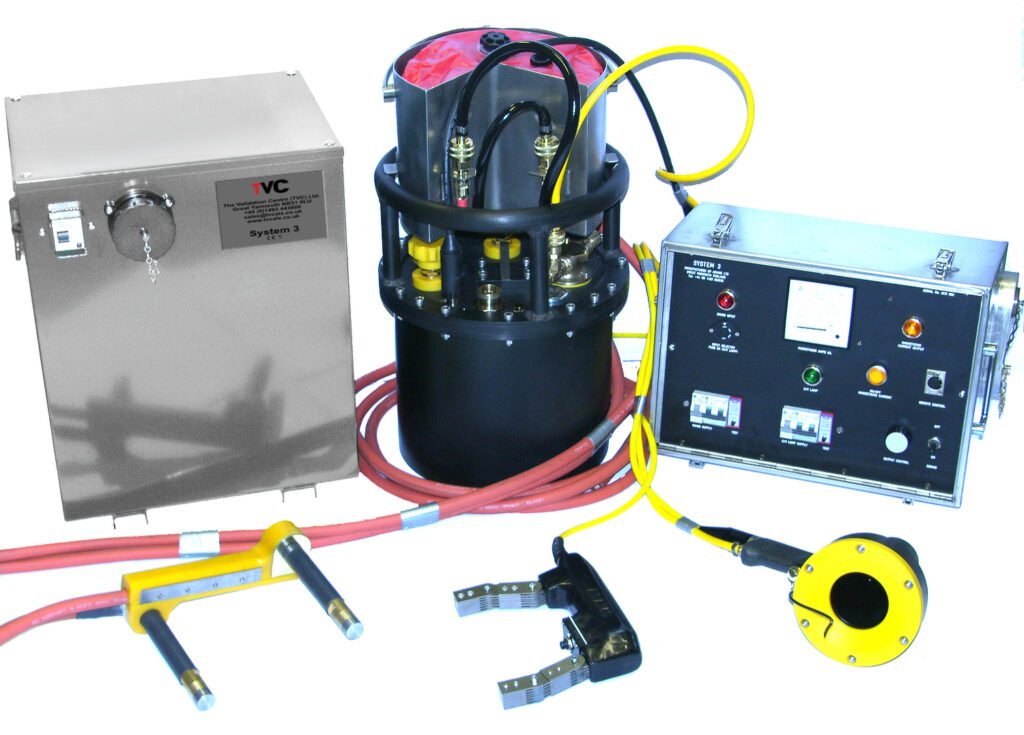
This method uses X-rays or gamma rays to produce an image of the object being inspected. It is particularly useful for detecting internal flaws such as cracks or voids.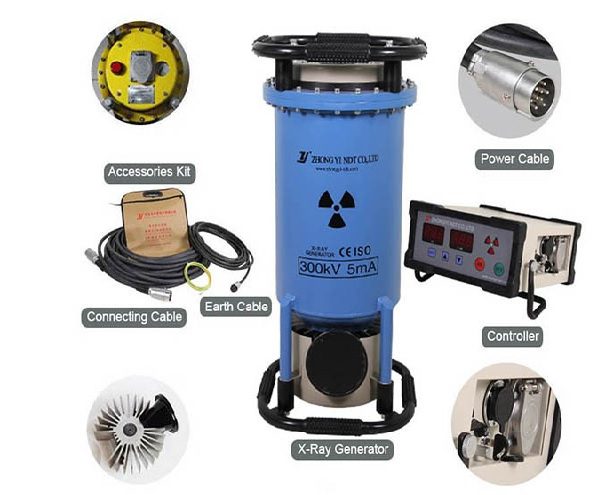




3-Ultrasonic testing
This involves sending high-frequency sound waves through the object being inspected and analyzing the echoes that are reflected back. It is useful for detecting defects such as cracks, voids, and delamination.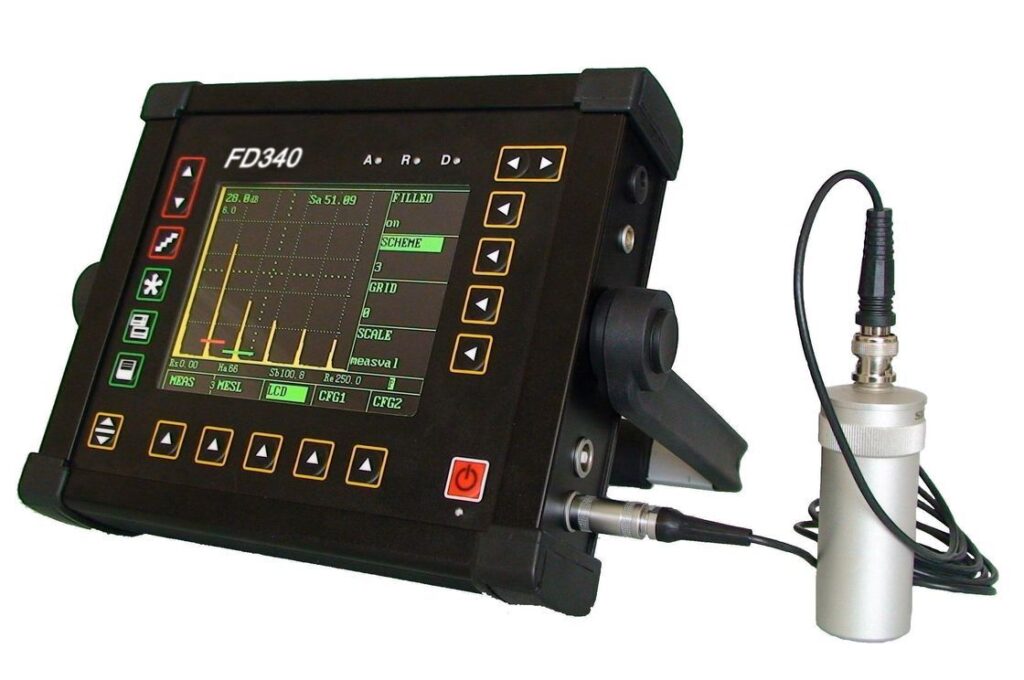




4-Magnetic particle testing
This method involves applying a magnetic field to the object being inspected and then sprinkling iron particles on the surface. Any defects in the material will cause the particles to cluster in certain areas, making them visible to the inspector.




5-Eddy current testing
This method involves passing an alternating current through a coil and placing it near the surface of the object being inspected. Any defects in the material will cause a change in the electromagnetic field, which can be detected by the inspector.




6-Acoustic Emission Testing (AET)
Monitors the high-frequency sound waves produced by materials or components under stress to detect cracks or other defects.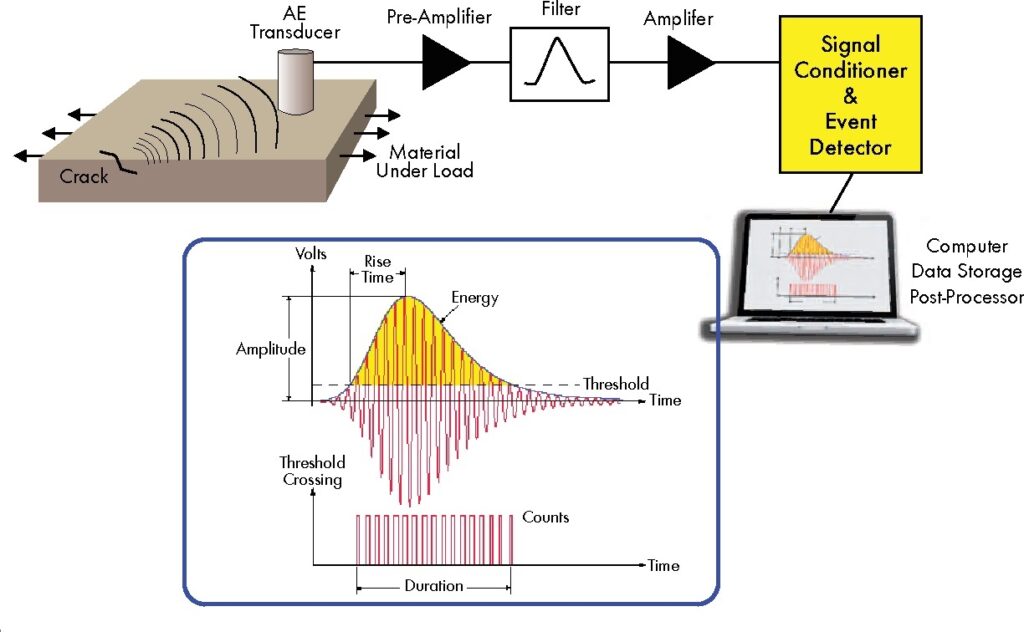




7-Infrared Thermography (IRT)
Uses thermal imaging cameras to detect temperature variations that could indicate flaws or defects in materials or components.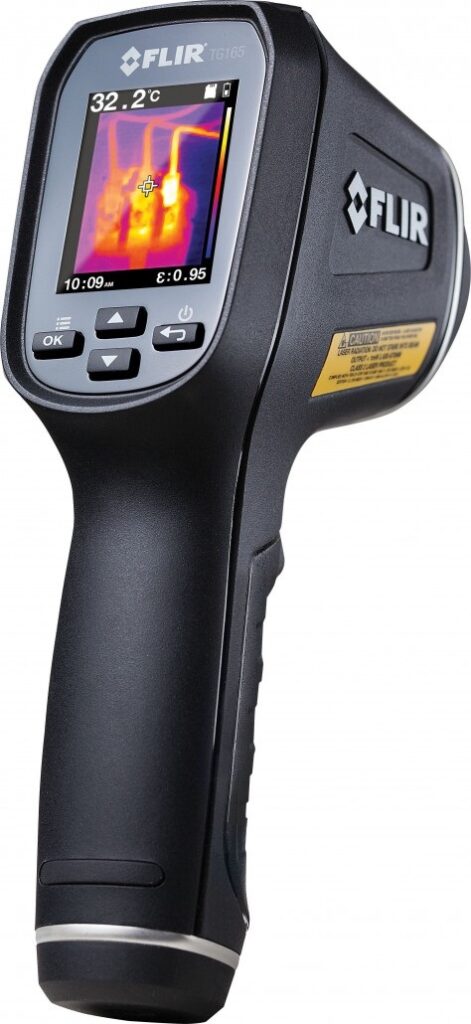




Application of NDT
NDT has a wide range of applications across many different industries, including aerospace, automotive, construction, manufacturing, and many others. Some of the most common applications of NDT methods include:
- Weld Inspection: NDT is commonly used to inspect welds in pipes, pressure vessels, and other components to ensure they meet quality standards and are free of defects.
- Structural Inspection: NDT methods such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to inspect buildings, bridges, and other structures for cracks, corrosion, and other defects.
- Aerospace: NDT is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of aircraft components such as engines, landing gear, and wings.
- Automotive: NDT methods are used to inspect engine components, gears, and other critical parts to detect cracks, corrosion, and other defects that could lead to failure.
- Oil and Gas: NDT is used to inspect pipelines, storage tanks, and other equipment to ensure they are safe and reliable.
- Manufacturing: NDT methods are used to inspect manufactured products such as pipes, valves, and other components to ensure they meet quality standards and are free of defects.
- Electrical Equipment: NDT methods such as infrared thermography are used to inspect electrical equipment such as transformers, switchgear, and motors to detect hot spots that could indicate problems.
Advantages of NDT
Non-destructive testing methods have many advantages that make them a valuable tool in a wide range of industries and applications. Some of the advantages of NDT include:
- Safety: NDT methods are non-invasive, which means that they do not damage the material or structure being tested. This makes them a safer alternative to destructive testing methods that can cause damage and potentially compromise the integrity of the component being tested.
- Cost Savings: NDT methods can detect defects and potential problems before they become more serious and require costly repairs or replacements. This can save money in the long run by avoiding downtime and reducing maintenance costs.
- Reliability: NDT methods are highly accurate and reliable, and can detect defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. This helps ensure the quality and reliability of the component being tested, and can help prevent accidents and failures.
- Versatility: NDT methods can be used on a wide range of materials and structures, including metals, plastics, composites, and concrete, among others. This makes them a versatile tool for many industries and applications.
- Environmental Friendliness: Because NDT methods are non-invasive, they do not produce any waste or hazardous materials, making them a more environmentally friendly option than some destructive testing methods.
Disadvantages of NDT
There are some potential disadvantages to consider. Some of these disadvantages include:
- Cost: NDT methods can be expensive, and the cost may be prohibitive for some applications or industries. Some NDT methods also require specialized equipment and trained personnel, which can add to the cost.
- Limited Detection: While NDT can detect many types of defects, it may not be able to detect all types of defects or problems, especially those that are very small or difficult to detect.
- Skill Requirements: NDT requires skilled personnel who are trained to perform and interpret the results of the tests. This can make it difficult to find qualified personnel, and the results may be less reliable if the personnel are not properly trained.
- Limited Accessibility: Some NDT methods require access to both sides of the component being inspected, which can be challenging in some situations, such as when inspecting pipelines or other components that are buried or difficult to access.
- False Positives: Some NDT methods can produce false positive results, meaning that they detect a defect or problem that does not actually exist. This can result in unnecessary repairs or replacement of components, which can be costly.
Read Also
- Thermal conductivity
- Column Chromatography
- What is NMR Spectroscopy?
- What is Spectroscope
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography | HPLC
- xnx gas detector calibration