Table of Contents
Calibration is a critical process in various industries to ensure accuracy and reliability of measurement instruments. Calibration equipment plays a crucial role in this process, helping to maintain the integrity and quality of measurements. In this article, we will explore the importance of calibration equipment, its types, how it works, key features to consider, benefits, common applications, maintenance procedures, challenges, emerging trends, and more.
Introduction to Calibration Equipment
Calibration equipment refers to tools and devices used to adjust, verify, or calibrate measuring instruments to ensure accurate and reliable readings. These instruments are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and more. Calibration equipment is essential for maintaining quality standards, complying with regulations, and ensuring consistency in measurements.
Importance of Calibration in Various Industries
Calibration is a critical process in various industries as it ensures that measuring instruments are accurate and reliable. Inaccurate measurements can result in faulty products, compromised safety, and regulatory non-compliance, leading to costly consequences. Calibration equipment plays a vital role in maintaining the accuracy and reliability of measuring instruments, which are used for quality control, research and development, testing, and production.
Different Types of Calibration Equipment
Calibration equipment comes in different types, depending on the nature of the instruments being calibrated. Some common types of calibration equipment include:
1.Calipers
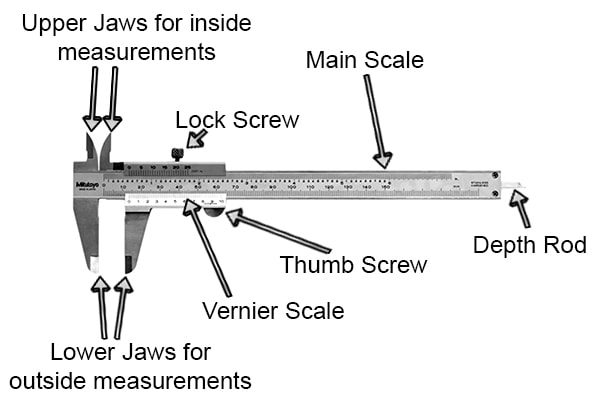
Calipers used to measure distances or dimensions with high precision.
2. Multimeters





Multimeters used to measure electrical quantities such as voltage, current, and resistance.
3. Pressure gauges





Pressure gauges used to measure pressure in various applications.
4. Thermometers





Thermometers used to measure temperature in different environments.
5. Torque wrenches





Torque wrenches used to apply torque to fasteners with precision.
6. Flow meters





Flow meters used to measure the flow rate of fluids in pipes or ducts.
7. Mass standards





Mass standards used to calibrate weighing instruments.
8. Optical instruments





Optical instruments used to calibrate optical measuring devices such as microscopes and spectrometers.
How Calibration Equipment Works
Calibration equipment works by comparing the readings of the instrument being calibrated with known reference standards. The calibration equipment generates known values, and the instrument being calibrated is adjusted accordingly to match these values. This ensures that the instrument provides accurate and reliable measurements.
Calibration equipment uses various methods for calibration, such as electrical, mechanical, optical, and thermal methods, depending on the type of instrument being calibrated. For example, electrical calibration equipment uses precise voltage, current, and resistance sources to calibrate electrical instruments, while mechanical calibration equipment uses precision gauges or standards to calibrate mechanical instruments.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing Calibration Equipment
When choosing calibration equipment, several key features should be considered to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. These include:
Accuracy and precision
The calibration equipment should provide high levels of accuracy and precision to ensure reliable calibration results.
Range and resolution
The calibration equipment should cover the required range of measurements and provide sufficient resolution for precise calibration.
Traceability and compliance
The calibration equipment should be traceable to national or international standards and comply with relevant regulations and standards.
Calibration procedures
The calibration equipment should have clear and well-defined calibration procedures that are easy to follow.
User-friendly interface
The calibration equipment should have a user-friendly interface that allows easy operation and navigation.
Calibration history and data management
The calibration equipment should have features for recording and managing calibration history and data for traceability and documentation purposes.
Calibration intervals and reminders
The calibration equipment should have the capability to set and manage calibration intervals and provide reminders for upcoming calibrations.
Calibration uncertainty
The calibration equipment should provide information about the uncertainty of measurements to ensure the accuracy of the calibration process.
Calibration certificate generation
The calibration equipment should have the capability to generate calibration certificates with all the necessary details for documentation and compliance purposes.
Benefits of Using Calibration Equipment
Using calibration equipment in industries and laboratories provides several benefits, including:
Improved accuracy and reliability
Calibration equipment ensures that measuring instruments are accurate and reliable, leading to consistent and quality measurements.
Compliance with regulations
Calibration equipment helps in complying with industry standards, regulations, and quality management systems.
Reduced risk of errors
Calibration equipment minimizes the risk of measurement errors, which can result in faulty products or compromised safety.
Enhanced product quality
Calibration equipment ensures that products meet the required quality standards, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Cost savings
Calibration equipment helps in identifying and addressing measurement discrepancies early, reducing rework, and minimizing costly consequences of inaccurate measurements.
Common Applications of Calibration Equipment
Calibration equipment is widely used in various industries and applications, including:
- Manufacturing: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate measuring instruments used in production processes to ensure quality control.
- Healthcare: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate medical devices such as thermometers, blood pressure monitors, and infusion pumps to ensure accurate patient care.
- Automotive: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate measuring instruments in automotive manufacturing processes to ensure safety and performance.
- Aerospace: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate measuring instruments used in aircraft manufacturing and maintenance processes to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
- Pharmaceuticals: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate measuring instruments used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to ensure compliance with strict quality standards.
- Research and Development: Calibration equipment is used in R&D laboratories to calibrate measuring instruments used in scientific research and experimentation.
- Environmental monitoring: Calibration equipment is used to calibrate instruments used for environmental monitoring, such as weather stations, air quality monitors, and water quality analyzers.
Calibration Equipment Maintenance and Calibration Procedures
Proper maintenance and calibration procedures are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of calibration equipment. Regular maintenance and calibration procedures may include:
- Cleaning and inspection of calibration equipment to remove dirt, debris, and other contaminants that may affect accuracy.
- Lubrication and adjustment of moving parts to ensure smooth operation and precise measurements.
- Verification of calibration equipment against known reference standards to ensure accuracy and traceability.
- Calibration of calibration equipment using traceable standards to ensure reliability and consistency in calibration results.
- Documentation of calibration procedures, results, and calibration certificates for traceability and compliance purposes.
- Calibration interval management to ensure that calibration equipment is calibrated at appropriate intervals based on industry standards and regulations.
- Calibration reminders and notifications to ensure timely calibration of the equipment.
Challenges and Limitations of Calibration Equipment
Despite their benefits, calibration equipment also has some challenges and limitations, including:
- Cost: Calibration equipment can be expensive to purchase, maintain, and calibrate, which may pose challenges for smaller businesses or laboratories with budget constraints.
- Complexity: Calibration equipment may require specialized knowledge and expertise to operate, maintain, and interpret calibration results accurately.
- Calibration uncertainty: Calibration equipment may have inherent uncertainties, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of calibration results.
- Environmental factors: Calibration equipment may be sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference, which may affect its performance, and require careful environmental controls during calibration procedures. 5. Calibration traceability: Ensuring traceability of calibration equipment to national or international standards may be challenging, especially for specialized or unique calibration requirements.
- Calibration frequency: Determining the appropriate calibration frequency for different types of instruments and equipment can be complex, and may require careful consideration of factors such as usage, environment, and regulatory requirements.
- Maintenance and repair: Maintenance and repair of calibration equipment may require specialized technical expertise and may result in downtime, impacting the calibration schedule.
- Compliance and documentation: Meeting regulatory and compliance requirements, such as ISO 17025 or FDA regulations, may pose challenges in terms of documentation, record-keeping, and audit trails.
Conclusion
Calibration equipment plays a critical role in ensuring accurate and reliable measurements in various industries and applications. It helps in maintaining product quality, complying with regulations, and reducing the risk of errors. However, it also comes with challenges and limitations such as cost, complexity, calibration uncertainty, environmental factors, traceability, calibration frequency, maintenance, and compliance requirements. Proper maintenance, calibration, and documentation procedures are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of calibration equipment.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is calibration equipment necessary for all industries?
Yes, calibration equipment is essential for industries that rely on accurate measurements for quality control, compliance, and safety purposes.
How often should calibration equipment be calibrated?
The calibration frequency depends on various factors such as the type of equipment, its usage, environment, and regulatory requirements. It is determined based on industry standards, manufacturer recommendations, and calibration history.
Can calibration equipment be calibrated in-house?
Yes, calibration equipment can be calibrated in-house if the necessary expertise, traceable standards, and documentation procedures are in place. However, third-party calibration services may also be utilized for certain specialized or critical calibration requirements.
What are the consequences of using uncalibrated measuring instruments?
Using uncalibrated measuring instruments can result in inaccurate measurements, faulty products, compromised safety, and non-compliance with regulations, leading to potential financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, and legal consequences.
How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of calibration equipment?
Regular maintenance, calibration against traceable standards, proper documentation, and compliance with regulatory requirements are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of calibration equipment.
Read Also