Table of Contents
What is Optical Pyrometer:
A pyrometer that measures temperature by measuring how much light of a certain wavelength is emitted by a hot body is called Optical Pyrometer.
The optical pyrometer is a thermometer of the non-contact variety. It operates under the premise that an object’s brightness must match the brightness of the filament that is housed inside the pyrometer. The temperature of the furnaces, molten metals, and other overheated materials or liquids are all measured using an optical pyrometer.
With the use of a contact type device, it is impossible to gauge the temperature of a highly heated body. So, their temperature is measured using a non-contact pyrometer.
Operating range:
Up to 1400°C, which can be increased to 3000°C by using an absorption-type screen put next to the lens.
Working Principle of Optical pyrometer:
It is based on a comparison between the visible radiation intensity (brightness) emitted by a heated body and the radiation energy emitted by a source with known intensity. In this instance, the radiation intensity of a hot body, the temperature of which is to be determined, is matched with the radiation intensity of a reference filament (lamp), the temperature of which is known.
Optical Pyrometer’s Construction and working
The hot body, lens, filament lamp, and red filter that are all lined up in a line make up the optical pyrometer (Fig. 1). It is focused on the reference filament using a lens to capture the radiant energy (lamp or bulb). Briefly, the lens creates a picture of the radiating source and aligns it with the reference filament (lamp or bulb). To modify the light intensity, current flowing through the reference filament (lamp or bulb) is changed. An eyepiece and a red filter are used to observe the filament.

When the picture on the filament and the image of the radiating source are of similar brightness, the current flowing through the filament is adjusted. With the use of a rheostat, the amount of current modification required to match the pictures of two light sources is accomplished. Temperature measurement is all that the current adjustment is. The rheostat position shown on the dial is graded according to temperature. Between the heating filament and the operator’s eye position is a red filter. The red filter serves as a barrier to keep out harmful radiations, which can cause operator eye disorders.
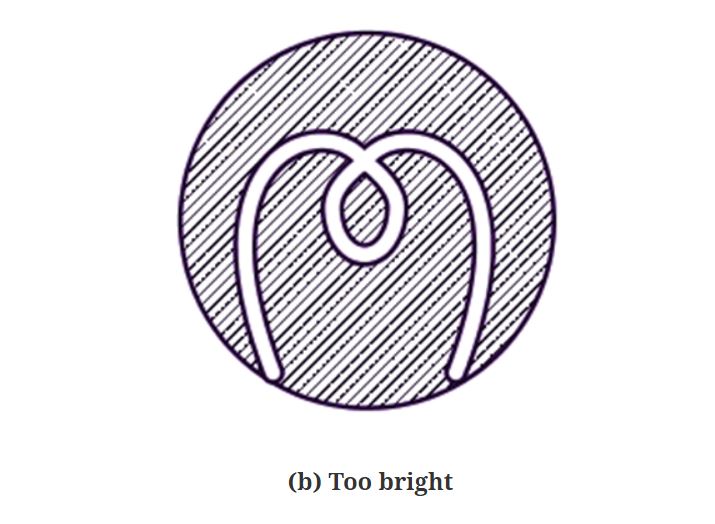
When the brightness of the image produced by the source and the brightness of the filament are both equal, the filament’s outline will display a pattern as depicted in Fig. 2. (a). However, if the filament temperature is higher than what is needed for equal brightness, the filament will become overly bright, as seen in Fig. 2. (b). The filament gets excessively black if the temperature is lower than what is needed for equivalent brightness, as seen in Fig. 2. (c).














Advantages of an optical pyrometer
Optical pyrometers are portable.
The device is easy to use because of its straightforward assembly.
Gives a highly accurate reading of +/-5 degrees Celsius.
Optical pyrometers have Rapid reaction(fast response)
Accurately measuring high temperatures is possible.
It is employed to measure temperature at a distance.
It is less susceptible to emissivity changes.
It can withstand temperatures of up to 3000°C, which is very high.
The distance between the two objects is not at all of a concern as long as the object’s size and the optical pyrometer’s size correspond. As a result, remote sensing can be done using the Optical Pyrometer.
Disadvantages of an optical pyrometer
Optical pyrometer is a costly device.
Increased likelihood of human error when changing the image.
It exclusively measures the surface temperatures of hot objects.
Behaviourally nonlinear.
Errors that could occur because of the presence of intervening gases or vapours that absorb radiation.
The pyrometer’s operation is reliant on how much light the heated body emits. Thus, the pyrometer is used to measure temperatures more than 700 degrees Celsius. It is not suitable to measure temperature below 700 deg C.
Adjusting the filament current affects the pyrometer’s accuracy.
The temperature of clean gases cannot be measured using a pyrometer, either.
Use of an optical pyrometer|Application of Optical Pyrometer:
Measuring the temperature of molten metal, etc.
Applications at very high temperatures, around 3000°C.
The temperatures inside the furnace can be measured.
It is employed for crucial process measurements in the semiconductor, medical, induction heat treatment, crystal development, furnace control, glass manufacturing, semiconductor, and other industries.
Difference Between Radiation Pyrometer and Optical Pyrometer
| Sr No | Point of Comparison | Optical Pyrometer | Radiation Pyrometer |
| 1 | Temperature Measurement Range | Optical Pyrometer can measure the Temperature from 700°C to 3000°C | Radiation Pyrometer mostly use to measure the Temperature Greater than 750 °C. |
| 2 | Sensitivity | Good | Fair |
| 3 | Calibration | Compared to the Standard tungsten strip light. | Compared to a Standard optical pyrometer. |
| 4 | Accuracy | Less | More |
| 5 | working | In comparison to the heating filament, the colour of the hot body. | Lenses focus radiant energy on the thermocouple’s hot junction. |
| 6 | Stability | Fair | Good |
| 7 | Output | a colour that is compared to a heating filament whose temperature is known. | Emf, which is calibrated to provide a hot body’s temperature. |
| 8 | Cost | High | Low |
Faqs:
1). What is a pyrometer, exactly?
The term “pyrometer” refers to a remote-sensing thermometer that measures surface temperature.
2). What is an optical pyrometer used for?
It is employed in a number of industrial applications to measure non-contact high temperatures.
3).What is the pyrometer’s operating system?
The pyrometer’s basic operation is to gauge an object’s temperature by sensing the heat or energy it produces without making direct contact.
4).What is the optical pyrometer’s measurement range?
Typical pyrometers have a working range of 700°C to 3,000°C.
5).What is a red filter used for?
The wavelengths band is narrowed by the employment of a red filter placed between the eyepiece and the reference bulb.
Recommended Articles