Table of Contents
The term “DCS” means Distributed control system. The term “Distributed “ refers to the fact that the system is section wise geographically distributed, Hardware wise distributed, Intelligence & Processing, Risk etc are term “ Distributed “. The control system performs a specified assigned control function with many sub systems. Each one of these sub system having its own processor and self contained software programmer wired directly to the field instruments by standard analog signal line or through field multiplexing wiring system (multiplexer). The processing in the subsystem is digital. The field signals are sent to the field and received from the field in analog form. DCS is connected with various subsystem by a communication network called “Data Highway “ which is capable of carrying information at high frequency to and from various sub system. Compared to the conventional pneumatic control, DDC systems were particularly helpful in speedy and precise control during start-up, shutdown and emergency periods. A process operator sitting on one console desk could efficiently control the entire process with greatly enhanced operational speed and precision.
The facilities were further extended to include automatic optimization of key process variables by computer linked supervisory control and overall on-line optimization of processes.
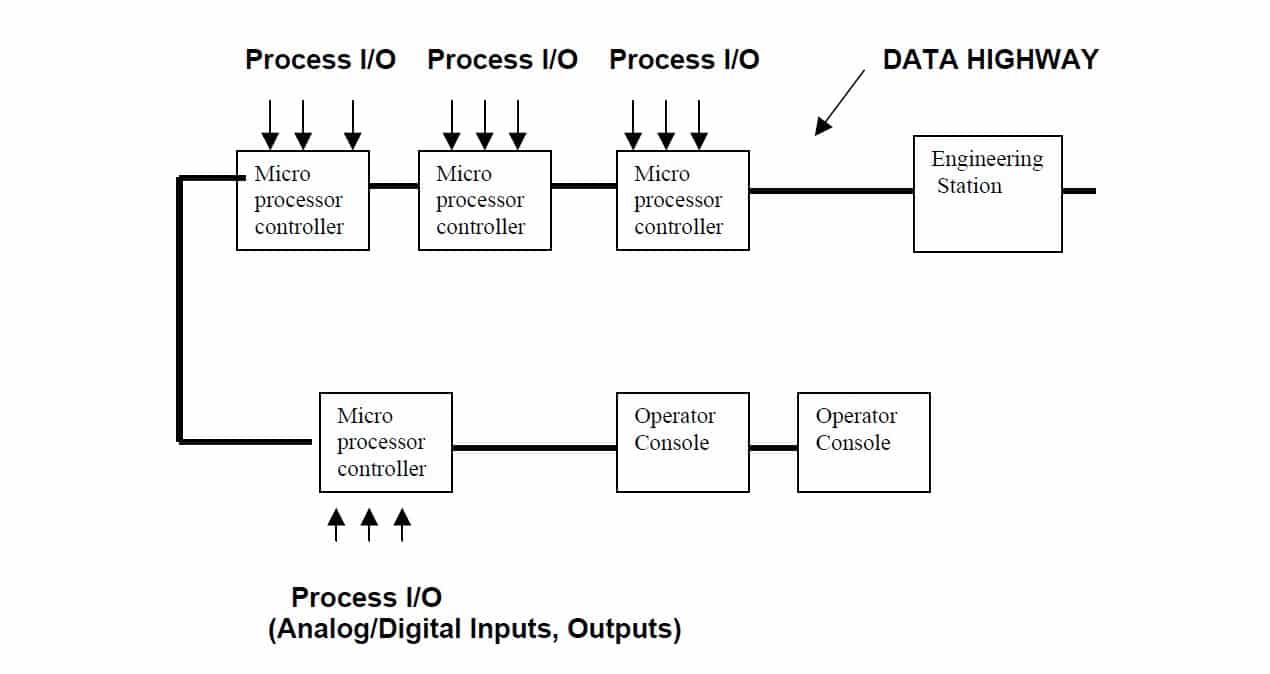
The schematic of the DCS system is shown in the above figure. Here the microprocessor controller receives the analog / digital signals from the field process the signal as per the configuration and sends the signal to the field. Here the processing is in the digital form .The analog signals are received and converted to the digital signal using ADC .The processed digital signals are converted into analog form using DAC. Each sub systems like controller unit, console, Engineering stations are connected through the Data Highway. This is the Basic concept of the DCS system.
Successful implementation of the advanced control schemes can result in multifold benefits for plants. These can be summed up as under:
- Quantifiable benefits
- Increased plant throughput
- Better management information on plant performance.
The advanced control and optimization concepts allow the selection of the most appropriate operating variables. In addition, they allow a more precise control of these variables so as to minimize the effects of disturbances there by improving the plant reliability The management obtains better information giving both economic and technical data, which highlights the most cost effective way of running the plant at any time. The information is communicated in an easily understood form comprising material balance, utility balance economic analysis, profit analysis etc.
Different types of Control systems and its evolution in to DCS System
- During the period of 1930 ‘s Machine type controllers were initially used in Railway steam engines also Manual type controllers were used in the Industries.
- During the period of 1940’s instead of Manual control , pneumatic signals were used for the control purpose. Large size pneumatic control panels were used.
- During the period of 1950’s the smaller size pneumatic control panels were used.
- During the period of 1960’s Small size analog controllers using analog devices operational amplifiers etc.
- During the period of late 60’s and early 70’s supervisory controllers with digital computers were used. In the supervisory control system the panel mounted loop controllers are connected to the supervisory computer through a gate way unit. The control can be done from both the computer as well as controllers. The digital computer is also used for monitoring, storing data. . The purposes of introducing computers were mainly data logging, set point control (SPC) at this first stageDuring the period of 1975 ~ DCS entered the market with CRT ‘s used for control. :
As discussed briefly earlier the various subsystems are connected through the data high way .And the controlling can be done from the console .Data is also stored in the storage device of the console. CRT is used for the control. As the introduction of computers into process control advanced, controller functions were superseded by computers, and DDC in which computers directly controlled processed began to be employed. In the early stages, the control system was centralized where a central computer did not process all process control functions but functioned mainly as a monitor. The most important reason was cost effectiveness.





- During the period of 1990~ the integrated management system having process control, production control and management information system started available in
the market. The integrated management system integrates process control, production control and management information under one system. Thse are more open to other systems with open system architecture. These systems apart from process control also provides process management, Product scheduling, Optimization, Production plan ,Inventory Management ,Cost accounting , Operational Plan etc. The roll of process control computers has been changing. In this background, lies the rapid growth of computer functions. Computer functions are said to increase ten times every ten years thereby also increasing its capacity and computation speed. Process control man-machine interfaces have also been changing with the times. These changes are shown in the following figure:
Working and Operation
In a DCS system, sensors operate to receive data and process the information, and transfer the data to local input/output modules where actuators are also connected to these I/O modules. With this connection, process parameters are managed exactly. The data received from here is collected and sent to the Process Control Section via a field bus. In the case of smart field devices, the sensory data will be transmitted directly to the process control section, and the collected data is then processed, evaluated, and produces results based on the control logic executed in the controller.
These results are now transmitted via the field bus to the actuator devices. Distributed control system alignment, authorization, and execution of control logic function at the engineering level. And the operator has the ability to view and transmit control actions to functional locations.
This is the brief working of distributed control system.
Structure and Architecture of Distributed Control System
In a DCS architecture, the control processing unit is distributed to all nodes present in the system and the entire system has increased reliability and minimizes failure of a single processor. When a single processor fails, the entire process will be affected by the failure in the centralized computer unit. The spread of computing power capability to racks connected to the I/O area also ensures for accelerated controller functionality by eliminating potential central and network operating delays. The structure of the DCS can be clearly explained at each level.





Level 0 – This level is included with field equipment such as control valves, temperature sensors and final control components such as flow elements.
Level 1 – This level includes technologically advanced I/O modules and their respective distributed types of electronic processors.
Level 2 – Here, regulators help collect data from processor nodes present in the computer system and then offer operator managed screens.
Level 3 – This is called the production-managed stage where it is not directly concerned with controlling the process but is involved in checking production and monitoring goals.
Level 4 – This is called the production scheduling stage.
Level 1 and Level 2 are considered as the operational phase of common type of DCS where all the components are covered under the integrated system of a single manufacturing person. Whereas Level 3 and Level 4 manages to control and schedule activities.
Whereas in the architecture of distributed control system, it mainly has three important features which are:
- Automation of industrial process by assimilating high-end control approaches.
- The arrangement of whole things as a whole
- Many control functions are distributed as small subsystems that are semi-autonomous in nature. They are interconnected using a high-speed communication bus and operations include data management, process control, data addressing, process examination, data reporting, accumulation and data retrieval.





Distributed Control System Architecture
The above three characteristics are clearly seen in the architectural diagram of a distributed control system. Here, there are 4 basic elements of a distributed control system:
Engineering Workspace
For DCS, these elements act as supervisory controllers. This can be a computer device or any personal computer with continuous engineering software like ABB Freelance Type DCS for Control Builder F engineering workspaces. This element provides controlling configuration tools that allow the user to conduct engineering activities such as development of new loops, creating multiple I/O points, changing control and sequential logic, configuration of multiple devices, and each I/O Document preparation for the component and many more.
HMI or Operating Workspace
This element is employed for efficiency, monitoring and management of plant parameters. It can be any monitoring device or even a personal computer that has a separate software device where the user can view the process factor values and perform functionality accordingly. These HMI units can be multiple or single units where single units are responsible for activities like displaying risky price and trend. While many units are responsible for some PC display factor, data acquisition and logging and trend record.
Process Controlling Unit
In a distributed control system, this element is called a local control unit, processing unit, or distribution controller. A DCS can contain one or more PC units that can be expanded using a variety of I/O units. The Process Control Unit consists of a powerful CPU section, a communication unit with extended field bus capability, and remotely connected I/Os. Field equipment such as actuators and sensors are connected to the I/O components for this unit. Some field equipment can connect directly to the field bus without being connected to the I/O module. A device that has this type of connection is called a smart field device.
Input to the PC unit is received from a number of sensors via the Input section, checks the received input and handles depending on the control logic executed, and controls the output through the Output section to relays and actuators. broadcasts to.
Communication Media
The media of communication serves as an important role in DCS. It links the engineering workspace, process unit, operations section and smart devices. It transmits the data to the stations. Common types of communication protocols used in DCS include Profibus, DeviceNet, Ethernet, Foundation Field Bus, and others.
It is not very necessary for the whole DCS to implement only one protocol, some tiers use only one network while some other tiers use different networks. For example, assume that field equipment, processing stations, and distributed input and output devices are interconnected using Profibus and the communication in the HMI unit, processing station, and engineering workspace is done using Ethernet as shown as follows Is:





An additional advantage of DCS is the redundancy of some or all of the level of control space. In many situations, complex processes are embedded with redundant types of controllers and redundant communication networks such that a problem in the major processing line does not affect observation and control activities due to the redundant processing unit.
These are the 4 fundamental elements in a distributed control system.
Important Features of DCS
The main features of a distributed control system are:
- Management of complex processes
- System Redundancy
- Many pre-defined functional blocks – DCS provides various algorithms, several standard application libraries, pre-defined and pre-testing activities to handle huge systems.
- The more advanced HMI design allows for the management and monitoring of complex systems and also acts as a centralized system of the entire DCS.
- Increased Scalability – The DCS architecture allows for greater flexibility that can be used for any range of server systems
- system protection
Read Also