Table of Contents
Star Topology | What is Star Topology: The star network topology is characterized as a networking topology in which components are connected to a central part, which is commonly referred to as the HUB, via independent cables. Because there are no directions between the devices, this architecture will not generate traffic congestion.
In this case, the controller acts as an exchange, which means that when a device wants to communicate with another device, it sends information to the controller, which then passes the data to the receiving device.
Each device in the star topology just needs one link and one input-output port to connect to a large number of others. In this case, the hub/switch is referred to as a server, and the nodes that connect to it are referred to as clients.
What is the central device in star topology?
Hosts are the nodes in a star architecture, and the connections used to connect them can be optical/twisted fibres, coaxial cables, or RJ-45 connectors. The network’s traffic regulation is handled by a central device known as a hub/switch.
The network’s performance is determined by the hub’s capabilities. There should be no new nodes added if the hub/switch is incapable of supporting multiple nodes.
Because the physical arrangement of nodes and hubs resembles a star shape, the network topology is known as STAR. There are four types of central Devices that can be employed in a star topology:
- Hub/Repeater ,
- Router/Gateway,
- Computer
- Switch/Bridge
Star network topology Explain In details:
When a host device wants to send information to another host, the information is first sent to a central hub, and then to the receiver host. As previously stated, the central hub might be a computer that simultaneously serves as a server.
Every node in this topology has a unique address that aids in message transmission and reception in the network. When a switch operates as a server, for example, it is used to store the complete addresses of nodes connected to it. When a certain node needs to send data, the switch recognises which node needs to send data since it contains all of the nodes’ addresses.
When the hub serves as a server, however, it lacks the ability to store addresses. In this situation, the hub sends messages to all nodes in the network, and the receiving device locates the transmission node’s matching address and gets the data.
When one of the nodes in the network fails, it has no effect on the other nodes, but when the central hub fails, the entire network goes down.
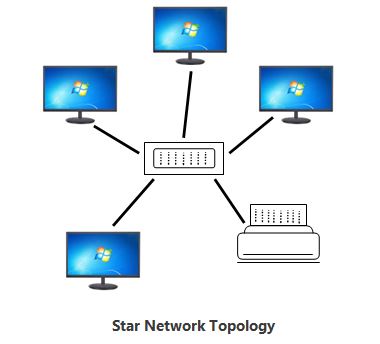
Star Topology Diagram:
Star Topology Diagram is as below.
Restarting the Hub:
The hub is considered either failed or overloaded when none of the star topology networks has access to network resources. In this situation, the reset switch must be pressed to reset the hub.
When resetting is required frequently, there is a risk of device failure or a network bandwidth limit being exceeded. As a result, based on the failed activity, the appropriate action must be taken.
Star topology advantages and disadvantages:
Following are the advantage and disadvantage of star topology
Advantages of star topology:
The following are some of the benefits of star topology:
- High reliability — When one node fails, it has no effect on the other nodes, and the rest of the network continues to function normally. As a result, this topology demonstrates excellent dependability.
- User-accessible — Here, nodes can be added and removed from the network without affecting the rest of the network. As a result, it appears that replacing nodes is simple and straightforward.
- Extended topology – By adding extra stars to the server, the length of the star network topology can be extended. The network, on the other hand, should be able to deliver power to all of the network’s activities.
- Enhanced efficiency — Because every device is connected to the server/hub via cable, the chances of data collisions are quite low. When compared to alternative network topologies, this also means that performance is better.
- It is safe to use since when a NIC fails or a cable is severed, it only affects one node. As a result, disabling the central core is the best way to disconnect all of the devices. It is the safest network structure because the central component is not immediately accessible to everyone.
Disadvantages of star topology:
The following are some of the drawbacks of star topology:
- Higher cost – Using a switch/router in a topology costs a lot of money.
- Increased maintenance — Because the hub is the heart of the system, it requires regular attention.
- Unmovable – Even if wireless topological connections exist, wired connections are the most common. This corresponds to the fact that a fixed cable length restricts individual mobility. As a result, productivity suffers.
- Minimal data transfer speeds — When this topology is managing large loads, a wired network connection works well. Furthermore, the wireless connection moves more slowly, indicating the possibility of blockages.
- More damage exposure – The star topology’s wires and cables have a significant potential for damage disclosure.
An example of a star topology:
An Ethernet network is a good example of star topology.
Where do star topologies come into play?
Star topologies are most commonly employed in residential networks, which are typically wireless connections, as well as in educational institutions and companies.
In a star topology, what kind of cable is used?
Coaxial cable or RJ-45 is utilised in the star topology network. It is entirely dependent on the type of network card installed on each computer.
Read Also
Point to point network topology