Table of Contents
What is maintenance?
Maintenance, usually, could be outlined as efforts taken to maintain the situation and efficiency of a machine all the time just like the situation and efficiency of the machine when it’s nonetheless new.
Maintenance actions can mainly be divided into two components: planned maintenance actions and unplanned maintenance actions.
Planned maintenance is maintenance that’s organized and carried out with thought to the long run, control and recording in accordance with the plans which have been decided beforehand.
The type of maintenance can’t be equated for every instrument, which is determined by the strategy, value and important stage. The following varieties of maintenance strategies are generally utilized in a number of industries.
- Preventive Maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
- Corrective Maintenance
- Breakdown Maintenance
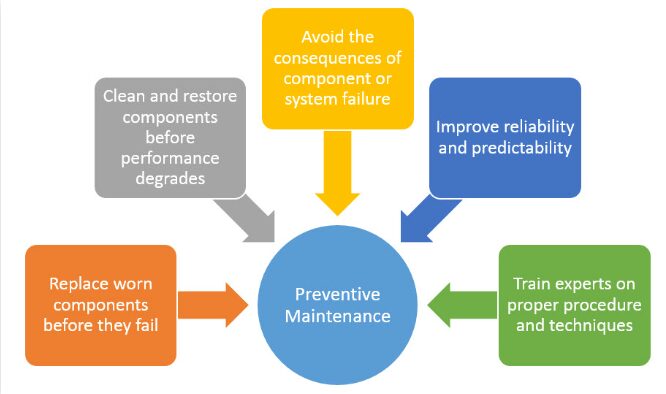
Preventive Maintenance(PM):
It is a technique for stopping harm to instrument by periodically changing components based mostly on time of use and finishing up minor maintenance and inspections to seek out out the present state of the tools / equipment.
Example: checking, Cleaning, lubricating,temperature monitoring, voltage monitoring, visual inspection, bolt tightening Periodic inspection Periodic and small over haul restorations.
Predictive Maintenance(PDM):
Predictive maintenance is a technique for doing maintenance by changing components based mostly on predictions utilizing a instrument. The point is that if the preventive methodology is barely based mostly on the schedule, then the predictive methodology relies on the results of the measurement.
This methodology may also use the 5 senses, for example in a shutdown valve, solenoid valve is making noise and generating heat. it can be feel by touching it.





Corrective Maintenance(CM):
It is a technique meant to enhance the reliability of instrument/machines by improvising. In addition to instrument it is usually meant for components which have a brief life cycle (scale back the frequency of harm) and speed up repair time.
In different phrases, this methodology is to increase MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) and speed up MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) due to its reliability (exercise to stop recurrence of harm) and maintenability (exercise to hurry up repair time).
Example: The operator has difficulty checking the level of the open tank in glass gauge so improvisation is done by making a measuring tape equipped with a desired scale.
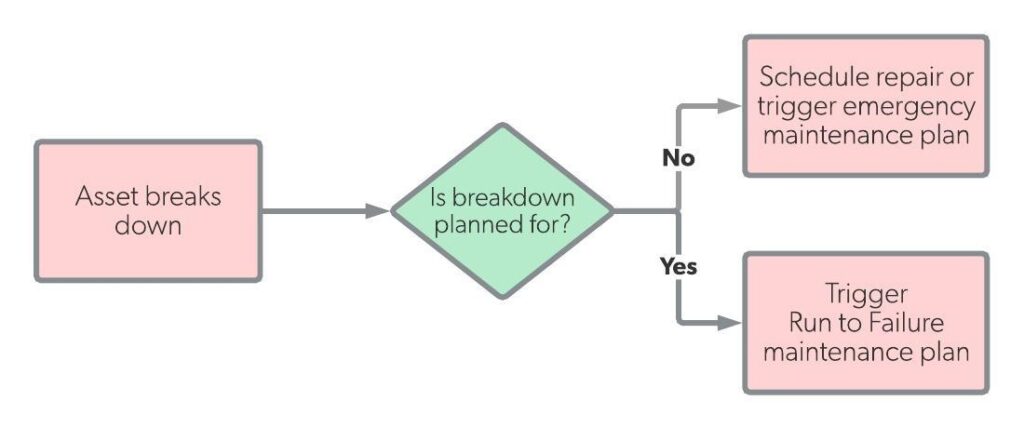
flowchart of corrective maintenance





Breakdown Maintenance(BDM)
It is a technique where inspection and alternative of components aren’t carried out, so with this methodology we depart the instrument damaged and then we repair it or exchange it.
Usually this methodology is utilized to instrument machines with consideration:
- Equipment is only elective (extra) in order that whether it is broken it doesn’t intrude with manufacturing
- The value of repairing / changing low-cost components
- Insignificant harm
- Easy and quick repair




Total productive maintenance (TPM):
Total productive maintenanc is a maintenance exercise that includes production operators in sustaining tools / equipment along with actions carried out by maintenance operators.
Examples are cleaning, lubricating, tightening nuts & bolts, dailly checking (checking instrument / machine state), easy repairs (changing leaking hoses, welding ideas) and so on.
The aims of the TPM are:
- Develop operators which are capable of detect harm alerts as early as potential. Because it’s the manufacturing operator that actually is aware of the state of the instrument to even essentially the most detailed half.
- Creating a neat, clear workplace in order that any irregularities could be detected as early as possible.