When a D.P. Transmitter is used for the purpose of measuring a level, it will be called a level transmitter. it is a common type of level measurement in industries. it’s level calculation is to simple that is given below.
ABC of Level measurement by using D.P. transmitter
The pressure at the base of a vessel containing liquid is directly proportional to the height of the liquid in the vessel. This is termed hydrostatic pressure. As the level in the vessel rises, the pressure exerted by the liquid at the base of the vessel will increase linearly.
P = SG*H
where
P = Pressure (Pa)
SG = Std. gravity of process liquid = ρg
H = Height of liquid column
ρ = Density
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2)
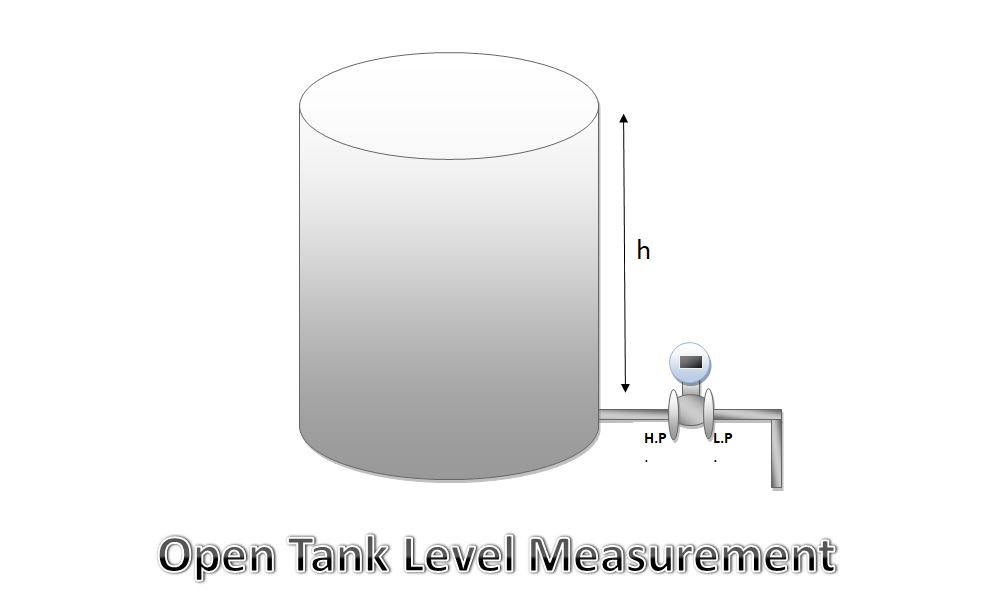
Open Tank Level Measurement
Open tank level is a basic level measurement . its calculation is very simple that is given below . Before calculation there are some steps for transmitter mounting and also shown in figure-
- Connect H.P. Tapping of transmitter to the base of tank.
- L.P. tapping of transmitter open to atmosphere.
- Now transmitter acts as simple pressure transmitter.

Pressure on H.P. tapping, PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*H)
Pressure on L.P. tapping, PL.P.= PAtm
Differential pressure, ΔP=PH.P. – PL.P
ΔP = PAtm+(SG*H) – PAtm
ΔP = SG*H
Calculation For LRV
The tank will be empty to get LRV, pressure on HP tapping and LP tapping is measured. When the tank is empty, the pressure exerted on HP tapping and LP tapping will be 0. because liquid height will be 0.
Putting H = 0 in ΔP = PAtm+(SG*H) – PAtm
PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*0) =PAtm
PL.P. = PAtm
LRV = PH.P. – PL.P = PAtm – PAtm
LRV=0
Calculation For URV
When Tank full filled with liquid (H), calculate Transmiiter Differential pressure (ΔP).
PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*H)
PL.P. = PAtm
URV = PH.P. – PL.P. = PAtm+(SG*H) – PAtm
URV=(SG*H)
Range = 0 to SG*H
Closed Vessel Level Measurement
Close vessel level measured with two type:-
- Dry leg level measurement
- Wet leg level measurement
Dry Leg Level Measurement
Level measurement in closed vessel done by dry leg method. This method is useful for all type liquids exclude vaporize. there are some steps to install transmitter and calculation formulas-
- Connect H.P. Tapping of transmitter to the base of vessel.
- Connect L.P. Tapping of transmitter to the top of vessel
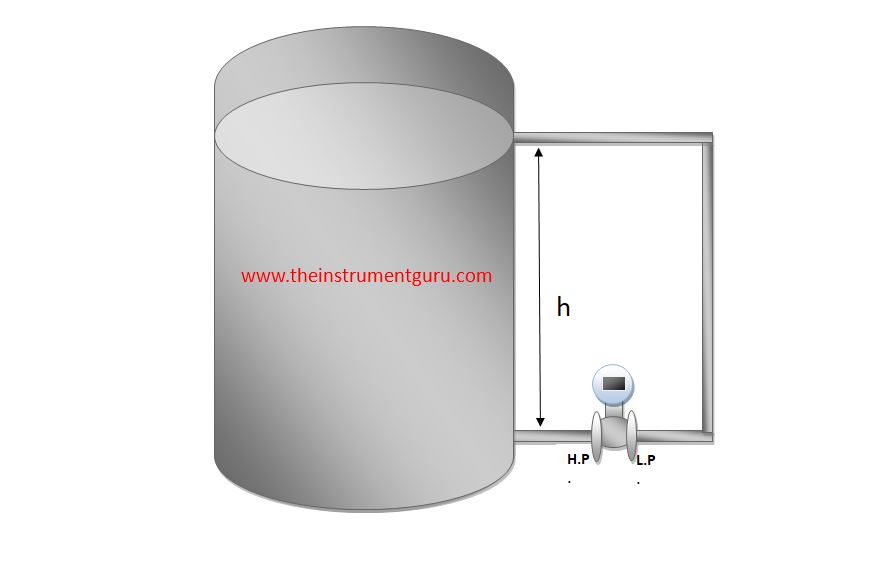




calculation :-
PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*0) =PAtm
PL.P. = PAtm
ΔP = PH.P. – PL.P. = (SG*H)
Calculation For LRV in Dry leg
PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*0) =PAtm
PL.P. = PAtm
LRV = PH.P. – PL.P = PAtm – PAtm
LRV=0
Calculation For URV
When Tank full filled with liquid (H), calculate Transmitter Differential pressure (ΔP).
PH.P. = PAtm+(SG*H)
PL.P. = PAtm
URV = PH.P. – PL.P. = PAtm+(SG*H) – PAtm
URV=(SG*H)
Range = 0 to SG*H
Wet leg level Measurement
Wet leg level measurement is used for vaporized liquid.
- Connect H.P. Tapping of transmitter to the base of vessel.
- connect L.P. Tapping of transmitter to the top of vessel.
- Fill LP impulse line with Known Density liquid according process demand.
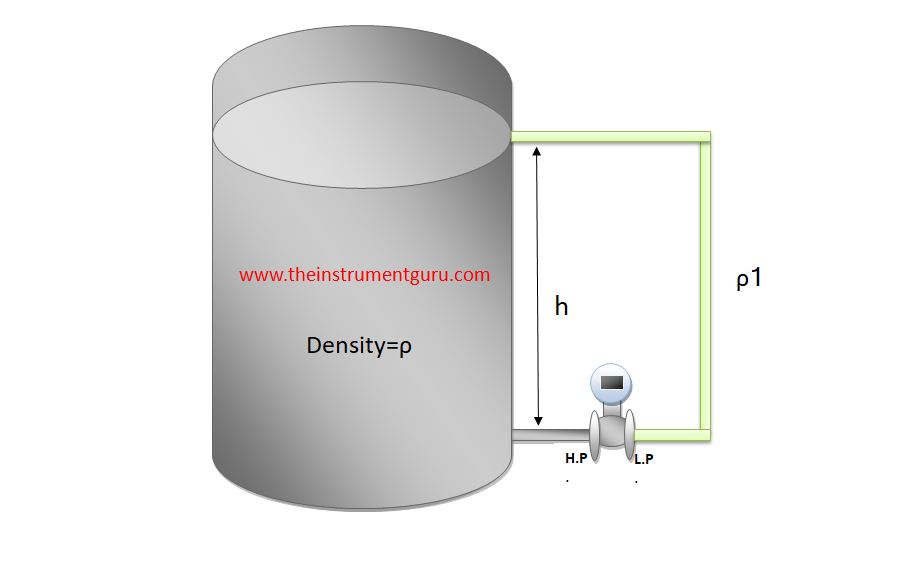




calculation :-
PHP = Pgas + (SGP*H)
PLP = Pgas+(SGf*h)
ΔP = Phigh – Plow = (SGP*H)-(SGf*h) or (ρp *g*H)-(ρf*g*h)
ΔP= (SGP*H)-(SGf*h) or (ρp *g*H)-(ρf*g*h)
Where:
SGP = Std. Gravity of process liquid.
SGf = Std. Gravity of filled liquid.
ρp= Density of process liquid.
ρf= density of filled liquid.





Calculation For LRV
When Tank empty (H=0), calculate Transmitter Differential pressure (ΔP).
calculation :-
Phigh = Pgas + (SGP*0)
Plow = Pgas+(SGf*h)
LRV= Phigh – Plow = (SGP*0)-(SGf*h) or (ρp *g*0)-(ρf*g*h)
LRV = -(SGf*h) or -(ρf*g*h)





Calculation For URV
When Tank full filled with liquid (H), calculate Transmiiter Differential pressure (ΔP).
calculation :-
Phigh = Pgas + (SGP*H)
Plow = Pgas+(SGf*h)
URV = Phigh – Plow = (SGP*H)-(SGf*h) or (ρp *g*H)-(ρf*g*h)
URV= (SGP*H)-(SGf*h) or (ρp *g*H)-(ρf*g*h)





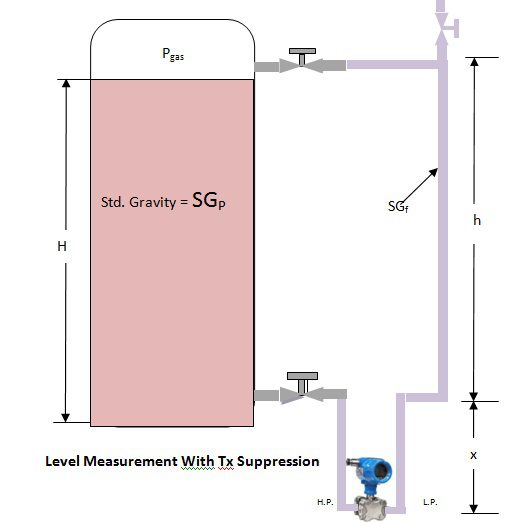
Transmitter suppression
In some cases, it is not possible to mount the level transmitter right at the base level of the tank. Say for maintenance purposes, the level transmitter has to be mounted X unit below the base of a vessel.
Phigh = Pgas + {SGP*(H+x)}
Plow = Pgas+{SGf*h+x)}
ΔP= Phigh – Plow = {SGP*(H+x)}-(SGf*h)
or {ρp *g*(H+x)}-{ρf*g*(h+x)}
ΔP= {SGP*(H+x)}-{SGf*h+x)}or {ρp *g*(H+x)}-{ρf*g*(h+x)}
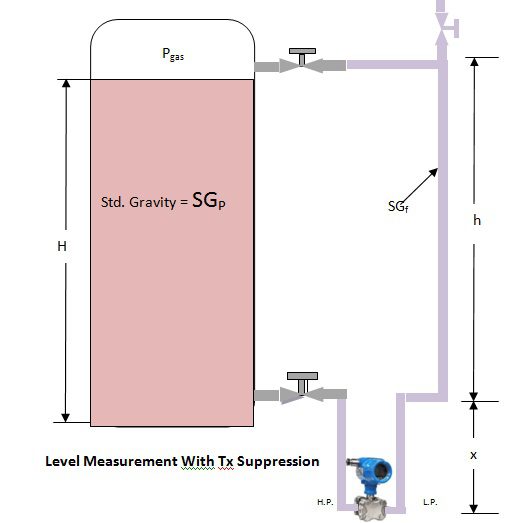




Calculation For LRV in suppression transmitter
When Tank empty (H=0), calculate Transmitter Differential pressure (ΔP).
Phigh = Pgas + {SGP*(0+x)}
= Pgas+(SGP*x)
Plow = Pgas+{SGf*(h+x)}
LRV = Phigh – Plow ={Pgas+(SGP*x)}-{SGf*(h+x)}or {ρp *g*x}-{ρf*g*h+x)}
LRV= {SGP*x)-{SGf*(h+x)}or (ρp *g*x)-{ρf*g*(h+x)}





Calculation For URV in suppression transmitter
When Tank empty (H), calculate Transmitter Differential pressure (ΔP).
Phigh = Pgas + {SGP*(H+x)}
Plow = Pgas+{SGf*h+x)}
= Phigh – Plow = {SGP*(H+x)}-(SGf*h)
or {ρp *g*(H+x)}-{ρf*g*(h+x)}
URV= {SGP*(H+x)}-{SGf*h+x)}or {ρp *g*(H+x)}-{ρf*g*(h+x)}




Transmitter Elevation (impulse line)
Transmitter mounted above the HP tapping point Is called Transmitter Elevation.
- Mount transmitter y above at H.P. Tapping of transmitter.
- connect L.P. Tapping of transmitter to the top of vessel.
- Fill LP impulse line with Known Density liquid according process demand.
calculation :-
Phigh = Pgas + {SGP*(H-y)}
Plow = Pgas+(SGf*h)
ΔP = Phigh – Plow = {SGP*(H-y)}-(SGf*h)
or {ρp *g*(H-y)}-(ρf*g*h)
ΔP= {SGP*(H-y)}-(SGf*h) or {ρp *g*(H-y)}-(ρf*g*h)
Where:
SGP = Std. Gravity of process liquid.
SGf = Std. Gravity of filled liquid.
ρp= Density of process liquid.
ρf= density of filled liquid.





Read Also