Table of Contents
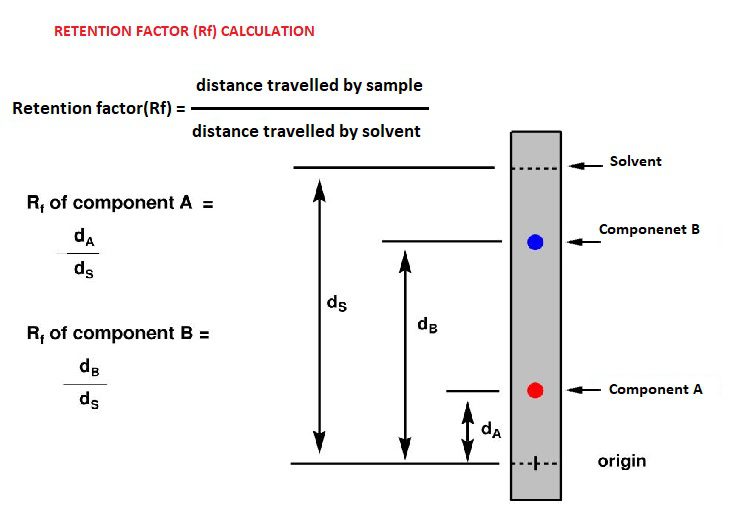
Thin layer chromatography definition-
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) can separate a mixture of amino acids and identify the test amino acids by measuring their Rf values. TLC is widely used laboratory technique and it is similar to paper chromatography. However, instead of using a stationary phase of paper, it involves a stationary phase of a thin layer of adsorbent like alumina, silica gel or cellulose. Compared to paper chromatography, it has the advantage of faster response, better separation. Chromatography is the process through which biomolecules from a complex mixture are separated and analyzed. This separation process consists of two phases a mobile phase and a stationary phase. In the mobile phase, the mixture is separated which is passed through the stationary phase. These two phases can be liquid-liquid or gas-liquid and solid-liquid. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a solid–liquid form of chromatography where the stationary phase is a polar absorbent and the mobile phase may be a single solvent or a combination of solvents. Because of the rapidity and simplicity of thin layer chromatography, it is often used to monitor the progress of organic reactions and to check the purify of products.
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) principle-
The separation depends on the relative affinity of the compounds for both phases. Compounds in the mobile phase move on the stationary phase surface. The movement occurs in such a way that compounds with higher affinity for the stationary phase move slowly while other(low affinity) compounds travel faster. Therefore, separation of the mixture is obtained. when the separation process is completed then the individual components from the mixture appear as spots at the respective levels on the plates. Their character and nature are identified by appropriate detection techniques. Finally this technique is used for to know the purity of the compound ,the progress of a reaction and to identify the various compounds present in the mixture.
Stationary phase in thin layer chromatography is silica gel, alumina and cellulose etc over glass/metal plate, plastic sheet etc.
Mobile phase in thin layer chromatography is developing solvent/ mixtures of solvents.
Thin Layer Chromatography Plates – Readymade plates are used which are chemically inert and stable. The stationary phase (silica gel, alumina and cellulose) is applied as a thin layer on its surface. The stationary phase on the plate has a finer particle size and is also of uniform thickness. Thin Layer Chromatography Chamber – Chamber used for developing plates. This is responsible for having a stable environment inside which will help spots develop. Also, it prevents evaporation of solvent and keeps the whole process dust free. Thin Layer Chromatography Mobile Phase – The mobile phase is the one that moves and contains the solvent mixture or solvent. This phase should be particle free. Thin layer chromatography metal sheet – This is to be placed inside the chamber. It is absorbed in the mobile phase.
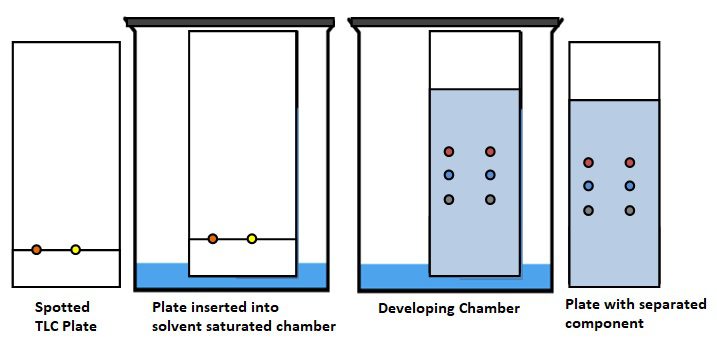
Thin layer chromatography diagram-
The diagram of thin layer chromatography is shown in the figure-
Thin marks are made on the bottom of the plate with the help of a pencil to mark the sample spots. A small amount spot of solution containing the sample is applied to a plate, The TLC plate is placed in the chamber where the sample spots do not touch the surface of the solvent in the chamber, and the lid is closed. The solvent moves up the plate by capillary action, meets the sample mixture and carries it to the plate (removes the sample). The plate must be removed from the chamber before the solvent front reaches the top of the stationary phase and then the plate dried. The sample spots can be detected through UV light chamber then according to visual color can be calculated retention factor Rf . Colored sample and uncolored sample can be detected through given some method.
- UV visualization, acid treatment, iodine vapor treatment, vallinin stain and ninhydrin treatment.
- In ultra violet visualization in this method detected that compound generate fluorescent in front of ultra violet rays example- Polyphenol.
- In Acid treatment, Plate separated with component dips in acid then air dried on it then after this plate do hot and generate a brown spot on the plate.
- Iodine vapor treatment treats the component in which the double carbon compound bond is present.
- Vallinin stain treats as alcohol, aldihyde and ketone.
- Ninhydrin treatment, if sample contain amino acid then this treatment is used.
Application of thin layer chromatography-
- Being a separation process, TLC is proven to be highly effective for separating pharmaceutical formulations that contain multiple components.
- This process can be used to check the purity of a given product.
- Medicines such as local anesthetics, analgesics, sedatives, hypnotics, anticonvulsant tranquilizers and steroids undergo TLC process for their qualitative testing.
- The cosmetic industry also uses TLC to check for the presence of preservatives in products.
- A given compound can be purified using thin layer chromatography and then compared with a standard sample.
- TLC also finds its use in biochemical analysis. Here, it can be used to separate biochemical metabolites from urine, blood plasma, serum, and body fluids.
- Like the cosmetic industry, the food industry also uses TLC to detect preservatives, artificial colors, and sweetening agents.
- The progress of a response can also be tracked with TLC to see if it is complete.
Advantage of thin layer chromatography-
The advantages of thin layer chromatography (TLC) are as follows
- Different spots of TLC can be viewed without any problem.
- This chromatography process is cost effective as compared to other methods.
- It can be used for many compounds, and does not take much time as it is quick.
- The process is much more straight forward than other methods.
- TLC makes it easy to analyze the purity parameters of any compound.
- Many compounds can be easily isolated via TLC.
Disadvantage of thin layer chromatography-
The disadvantages of thin layer chromatography (TLC) are as follows
- The TLC process cannot be used for low detection limit experiments because of its high detection limit.
- The plates used in TLC do not have a much extended stationary phase.
- Reproducing results in TLC is challenging.
- TLC is limited to qualitative analysis, and cannot be used for quantitative analysis.
- The separation length is also restricted compared to other chromatography methods.
- Here the process does not happen in a closed system. Therefore, factors such as temperature and humidity can affect the results, making them inaccurate.
Click on the below links to read more about-