Table of Contents
In the world of instrumentation and control systems, valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of fluids and gases. Two types of valves commonly used in such circuits are Quick Exhaust Valves (QEV) and Air Operated Valves (AOV). These valves offer unique functionality and are essential for ensuring the efficient operation of various industrial processes. In this article, we will explore the features, applications, and benefits of Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves in instrumentation circuits.
Introduction to Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves
Valves are critical components in instrumentation circuits as they control the flow of fluids and gases. Quick Exhaust Valves (QEV) and Air Operated Valves (AOV) are two types of valves commonly employed in industrial processes. These valves offer distinct advantages and are designed to meet specific requirements.
Understanding Quick Exhaust Valves

How Quick Exhaust Valves Work
Quick Exhaust Valves are designed to rapidly exhaust compressed air from a pneumatic system. They are typically used in applications where the quick release of air pressure is necessary. These valves are installed in the exhaust port of pneumatic actuators, allowing faster response times and increased operational efficiency.
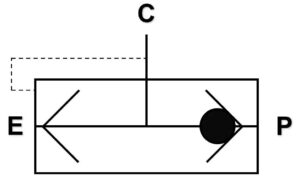




Advantages of Quick Exhaust Valves
- Improved Actuator Response: By quickly exhausting the air from the actuator, Quick Exhaust Valves enable faster actuation and response times, reducing cycle times in industrial processes.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Quick Exhaust Valves minimize air loss and wastage, leading to improved energy efficiency in pneumatic systems.
- Noise Reduction: The rapid exhaust feature of these valves helps reduce noise levels, creating a quieter working environment.
Exploring Air Operated Valves





Operating Principle of Air Operated Valves
Air Operated Valves use compressed air to actuate the valve mechanism. They are widely used in applications requiring remote control and automation. These valves provide a reliable and efficient method of controlling fluid and gas flow in industrial processes.





Benefits of Air Operated Valves
- Versatility: Air Operated Valves can handle a wide range of fluids and gases, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications.
- Fail-Safe Operation: In the event of a power failure, Air Operated Valves can maintain their position, ensuring safety and preventing process disruptions.
- Precise Control: These valves offer excellent control over flow rates and can be modulated to achieve the desired process parameters.
Applications of Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves
Quick Exhaust Valve Applications
- Pneumatic Actuators: Quick Exhaust Valves find extensive use in pneumatic systems controlling actuators in manufacturing processes, robotics, and automation.
- Presses and Clamps: These valves are employed in applications where quick release of air pressure is required for efficient operation of presses and clamps.
Air Operated Valve Applications
- Process Control Systems: Air Operated Valves are widely utilized in process control systems to regulate the flow of fluids or gases based on predefined parameters.
- Safety Systems: These valves play a vital role in safety systems by controlling emergency shutdowns, relief valves, and fail-safe operations.
Importance of Valves in Instrumentation Circuits
Valves are integral to instrumentation circuits as they facilitate precise control and regulation of fluid and gas flow. They ensure the stability and efficiency of various industrial processes by modulating pressure, temperature, and flow rates. Proper selection and installation of valves are crucial for the optimal functioning of instrumentation circuits.
Factors to Consider when Selecting Valves for Instrumentation Circuits
When choosing valves for instrumentation circuits, several factors should be taken into account:
- Fluid or Gas Characteristics: Consider the nature, corrosiveness, viscosity, and temperature of the fluid or gas that the valve will handle.
- Pressure and Flow Requirements: Determine the operating pressure and flow rates required for the specific application.
- Valve Size and Type: Select the appropriate valve size and type based on the system requirements, space limitations, and compatibility with other components.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the valve materials are compatible with the process media to prevent corrosion or contamination.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and presence of hazardous substances.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves
Installing Quick Exhaust Valves
- Identify the exhaust port of the pneumatic actuator and install the Quick Exhaust Valve securely.
- Ensure proper alignment and tight connections to prevent air leaks.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines and torque specifications during installation.
Installing Air Operated Valves
- Determine the optimal location for the Air Operated Valve considering accessibility and operational requirements.
- Follow the provided installation instructions and connect the valve using suitable fittings and adapters.
- Perform thorough testing and leak checks before commissioning the valve.
Maintenance Best Practices
- Regularly inspect valves for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Clean and lubricate valves according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Keep a record of maintenance activities and schedule preventive maintenance to avoid unexpected failures.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Valves in Instrumentation Circuits
Leakage Problems
If a valve is experiencing leakage, consider the following steps to troubleshoot:
- Check for loose connections or damaged seals and gaskets.
- Inspect the valve for debris or foreign particles that may be interfering with the sealing mechanism.
- Replace worn-out or damaged components as necessary.
Valve Sticking
If a valve is sticking or not operating smoothly, try the following:
- Clean the valve and remove any obstructions or buildup that may be causing the sticking.
- Lubricate the moving parts with a suitable lubricant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check for damaged or worn-out internal components and replace them if needed.
Inconsistent Performance
If a valve’s performance is inconsistent, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Verify that the valve is properly sized for the intended flow rates and pressures.
- Check the control signals and pneumatic connections to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Inspect the valve for wear or damage that may be affecting its performance and replace any faulty components.
Example: Pneumatic Actuation System in an Automated Packaging Line
In an automated packaging line, Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves are utilized in a pneumatic actuation system to control the movements of robotic arms for efficient and precise packaging operations.
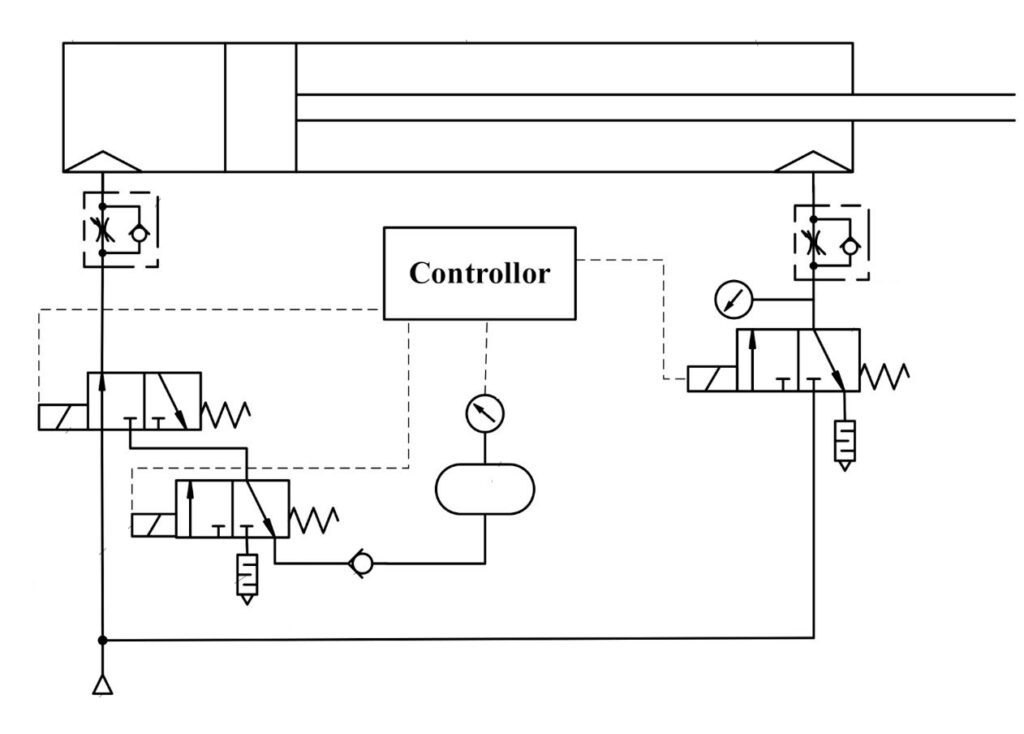




- Pneumatic Actuator: A pneumatic actuator, such as a pneumatic cylinder, is responsible for the linear movement of the robotic arm. It operates using compressed air as the driving force.
- Quick Exhaust Valve: A Quick Exhaust Valve is installed at the exhaust port of the pneumatic actuator. When the actuator needs to retract or release quickly, the Quick Exhaust Valve rapidly exhausts the compressed air from the actuator.
- Control System: The control system, which includes sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and human-machine interfaces (HMIs), receives signals and commands for the robotic arm’s movements.
- Command for Actuation: When a command is received to move the robotic arm, the control system sends a signal to the Air Operated Valve connected to the pneumatic actuator.
- Air Operated Valve Operation: The Air Operated Valve is designed to control the flow of compressed air to the pneumatic actuator. When the command is received, the Air Operated Valve opens, allowing the compressed air to flow into the actuator, causing it to extend.
- Quick Exhaust Valve Activation: Simultaneously, the Quick Exhaust Valve is activated to close the exhaust port of the actuator. This prevents the compressed air from escaping through the exhaust port and redirects it to the Quick Exhaust Valve instead.
- Quick Exhaust Valve Function: Once the robotic arm reaches its desired position, and there is a need for quick retraction or release, the control system sends a signal to the Quick Exhaust Valve. The Quick Exhaust Valve rapidly opens, allowing the compressed air inside the actuator to exhaust quickly.
- Rapid Actuation: As the compressed air is rapidly expelled through the Quick Exhaust Valve, the pneumatic actuator retracts or releases at an accelerated pace, enabling swift and precise movements of the robotic arm.
- Repetition of the Process: The process repeats for subsequent movements and packaging operations, ensuring efficient and timely handling of products on the automated packaging line.
By incorporating Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves into the pneumatic actuation system, the automated packaging line can achieve faster cycle times, improved productivity, and accurate positioning of the robotic arm, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of
Conclusion
Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves play vital roles in instrumentation circuits by ensuring efficient fluid and gas flow control. Quick Exhaust Valves enable rapid response times, increased productivity, and energy efficiency. Air Operated Valves provide precise control and reliable operation in various industrial applications. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of these valves are essential for optimal performance and safety in instrumentation circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves?
Quick Exhaust Valves are designed to rapidly exhaust compressed air, while Air Operated Valves use compressed air to actuate the valve mechanism. Quick Exhaust Valves focus on quick response times, while Air Operated Valves offer precise control and automation capabilities.
Can Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves be used interchangeably?
Quick Exhaust Valves and Air Operated Valves serve different purposes and cannot be used interchangeably. Quick Exhaust Valves are specifically designed for rapid exhaust, while Air Operated Valves are used for fluid and gas flow control.
How do I determine the correct valve size for my instrumentation circuit?
The correct valve size depends on factors such as flow rates, pressure requirements, and the characteristics of the fluid or gas being handled. Consult valve sizing charts, manufacturer guidelines, or seek assistance from a qualified engineer to determine the appropriate valve size for your specific application.
Are Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves suitable for hazardous environments?
Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves can be designed to meet the requirements of hazardous environments. Ensure that the valves are specified and certified for use in such environments to maintain safety and compliance.
Where can I find high-quality Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves for my applications?
High-quality Quick Exhaust and Air Operated Valves can be sourced from reputable valve manufacturers, distributors, or suppliers specializing in industrial instrumentation components. Conduct research, read customer reviews, and consider recommendations from industry professionals to ensure you choose reliable and durable valves for your applications.
Read Also
- Troubleshooting common Control Valve Problems
- How to Solve On-Off Valve Problems ?
- Control valve Leakage Problem
-
Calibration Techniques | Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability in Measurements