Table of Contents
Exploring the Benefits and Limitations of Proximity Sensors in Modern Technology
Proximity sensors are an essential component of modern technology, playing a crucial role in a range of applications. These sensors work by detecting the presence or absence of an object within a certain distance, without requiring physical contact. In this article, we will explore how proximity sensors work, their applications, and their benefits and limitations.

Proximity are electronic devices that are designed to detect the presence or absence of an object in their proximity without any physical contact. These sensors work on the principle of electromagnetic or ultrasonic waves, and they are widely used in various industries for automation and control applications.
There are several types of proximity sensors, including inductive, capacitive, magnetic, ultrasonic, and photoelectric sensors. However, the basic operating principle of all these sensors is the same, which is to detect the presence or absence of an object in their proximity.
Inductive sensors operate by generating an electromagnetic field and detecting changes in that field caused by the presence of a metallic object. Capacitive sensors work by detecting changes in an electrostatic field caused by the presence of an object with a different dielectric constant than the surrounding material. Magnetic sensors detect changes in a magnetic field caused by the presence of a magnetized object.
Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the sound waves to bounce back from an object, while photoelectric sensors emit a beam of light and detect changes in the amount of light reflected back from an object.
In all cases, the sensor detects the presence or absence of an object by measuring changes in a physical parameter, such as electromagnetic fields, electrostatic fields, magnetic fields, sound waves, or light. The sensor then sends a signal to a control system to trigger an action, such as opening or closing a valve, or stopping or starting a motor.
What are Proximity Sensors?
Proximity sensors are devices that detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain distance. They work by emitting an electromagnetic field or a beam of radiation, which interacts with the object and generates a signal that is used to determine its presence or absence. Proximity can detect a variety of objects, including metal, plastic, and liquids, and are commonly used in industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.





How Do Proximity Sensors Work?
Proximity sensors work by emitting a signal and detecting the changes in that signal when an object is present within the sensor’s detection range. The signal emitted by the sensor can take several forms, including magnetic fields, infrared radiation, ultrasonic waves, and capacitive fields.
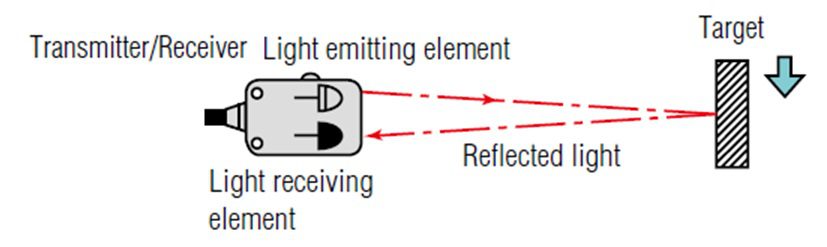




Magnetic field sensors work by generating a magnetic field and detecting changes in that field when an object is present. Infrared sensors emit a beam of infrared radiation, which reflects off an object and is detected by the sensor. Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves, which bounce off an object and are detected by the sensor. Capacitive sensors work by measuring changes in the electrical field around the sensor when an object is present.
Applications of Proximity Sensors
Proximity have a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics. They are commonly used in:
- Automotive: they are used in vehicles for obstacle detection, parking assistance, and collision avoidance.
- Industrial: they are used in manufacturing and production processes for detecting the position of objects, controlling robotic arms, and monitoring conveyor belts.
- Consumer electronics: Proximity are used in smartphones and tablets for detecting the proximity of the user’s face during phone calls and adjusting the screen brightness accordingly.
- Security: they are used in security systems for detecting the presence of intruders and triggering alarms.
Benefits and Limitations of Proximity Sensors
The benefits of proximity include:
- Non-contact detection: Proximity sensors do not require physical contact with the object being detected, making them ideal for applications where contact may be undesirable or impossible.
- High accuracy: Proximity sensors can detect objects with high precision, making them suitable for applications where precise measurements are required.
- Durability: they are built to withstand harsh environments and can operate in extreme temperatures and conditions.
However, proximity sensors also have some limitations, including:
- Limited range: Proximity have a limited detection range, which means that they may not be suitable for applications where detection over a long range is required.
- Interference: Proximity can be affected by electromagnetic interference, which can result in false readings.
- Cost: Proximity can be expensive, especially when high accuracy and precision are required.
Conclusion
Proximity sensors are an important component of modern technology, with a wide range of applications in automotive, industrial, consumer, and security systems. Understanding how proximity sensors work and their benefits and limitations is crucial for selecting the right sensor for your application. Whether you are designing a manufacturing process or developing a new consumer product, proximity sensors can help you achieve better accuracy, efficiency, and performance.
Read Also