Table of Contents
Various sensing devices are used by industries including the food, paper, pharmaceutical, chemical, petrochemical, fertilizer, power plant, paints industry, rubber, plastic and other sectors to measure the temperature in their workplaces. To measure temperature, we use thermometers. They are frequently utilised in business and industry because they are available everywhere and are reasonably priced. A thermometer is a mechanical instrument that uses a different principle in various applications to measure and monitor temperature rise. In the aforementioned sector, temperature is a crucial factor because the temperature more or less directly influences product. Therefore, today’s article will explain what a bimetallic thermometer is, how it is made, how it operates, what types there are, etc.
What is bimetallic thermometer?:
A thermometer is a tool that transforms temperature changes into mechanical displacement using two separate metal strips. Steel, copper, and brass are the metals that are utilised to make the thermometer. When heated, these strips, which are joined together, expand at various speeds.
Metals expand differentially as a result of temperature changes, hence bimetal thermometers are based on this functional principle. Two distinct metal strips with various heat expansion coefficients make up a bimetal thermometer.
Working principle of bimetallic thermometer:
Two key ideas are applied by bimetallic thermometers:
- With a change in temperature, all metals either expand or shrink.
- Because all metals have not the same temperature coefficients of expansion, their rates of expansion or contraction vary. It is possible to create deflections that are proportional to temperature changes by using the property of different rates of thermal expansion.
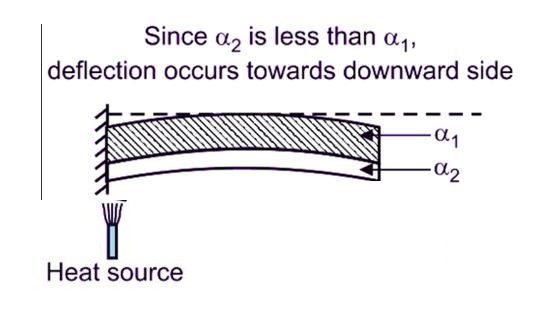
A bimetallic thermometer is composed of a bimetallic strip that is made by joining two thin strips of two different metals so that they are immobile with respect to one another. Bimetallic strips can be organised in a number of different ways, including flat, spiral, single-helix, and multiple-helix arrangements. As the temperature being applied to it increases, the free end of the bimetallic strip will deflect. According to each metal’s unique coefficient of thermal expansion, length will vary. A bimetallic strip will bend at its free end, but in the direction of the metal’s side that has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, since one end of the strip is fixed. If the temperature drops, the process will reverse. Free end deflection is directly proportional to two values,
- Square of a metal strip’s length and,
- A temperature change.
A bimetallic strip in the shape of a straight cantilever beam is shown in Figure “a”. The shift in temperature causes the free end to deflect when one end is Fixed is shown in figure”b”.





Bimetallic thermometer construction:
Bimetallic stripes are used to create this thermometer. It is related to the development of varied thermal expansion coefficients. As already said, it is a mechanical device that can be utilised to enable switching processes to provide electronic output by mechanical action.
These two metal strips are connected using a variety of techniques, including welding, bolting, riveting, and fastening. This strip can be manufactured of steel, copper, brass, etc.
Factors that affects the Response of the Bimetallic Thermometer’s Temperature Sensing Element:
- Heat transfer coefficient values.
- Whether the temperature detecting element has low or high thermal conductivity,
- The accuracy of measuring devices may be negatively impacted by changes in physical dimensions caused by temperature changes.
- Surface area per mass of the temperature sensing component
Bimetallic thermometer temperature range:
Bimetallic thermometers are used to measure the temperature range from 30°C to 550°C.
Types of Bimetallic Thermometer:
- Helical or Helix Type Bimetallic Thermometer
- Spiral Strip Type Bimetallic Thermometer
Helical Bimetallic Thermometer or Helix Bimetallic Thermometer | Helix Thermometer
In several industries, helical type bimetallic thermometers are used. helical type bimetallic thermometers are very useful where Separating the pointer from the bimetallic coil may be necessary in particular circumstances. The temperature measurement sensor must remain inside the pipe, and it is possible to show the temperature on the pipe’s outside.
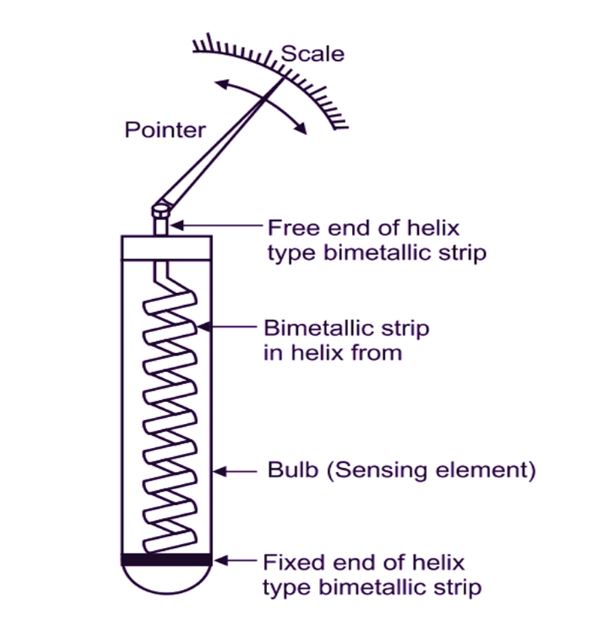




Image Displays Helix-shaped bimetallic thermometers are made by winding a strip of metal around another metal. Helix is attached to the bulb’s case on one end and the pointer on the other end. The bimetallic helix unwinds when heated due to the different rates of thermal expansion of the metals. As a result, the pointer glides or sweeps across a circular scale to display the temperature readings.
Helical bimetallic thermometer temperature range:
It can be used to measure the temperature from 30°C to 300°C.
Application of Helical Bimetallic thermometers:
Utilizing to measure the temperature in industries.
Helical Bimetallic thermometers are employed in refineries, hot tanks, and water heaters, among other places.
These thermometers are utilised in a variety of products used in homes and businesses, including air conditioners, ovens, heating wires, refineries, tampering tanks, heaters, etc.
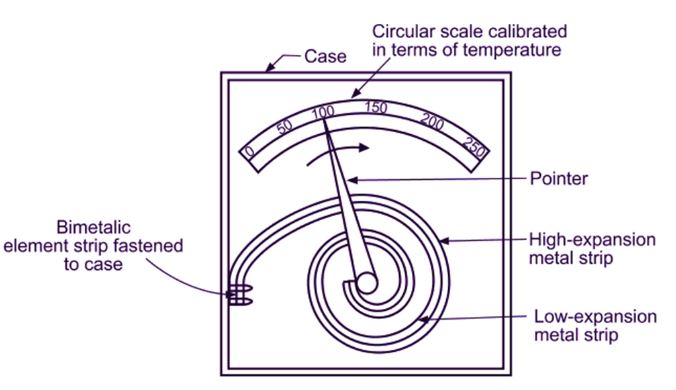
Spiral Bimetallic Thermometer:
A spiral bimetallic thermometer is depicted in figure. In this thermometer, the pointer mounted in a housing with a scale is attached to the spiral bimetallic (strip) element. When heated, the spiral bimetal rotates in a clockwise direction and bends in the direction of a metal with a low thermal coefficient of expansion. As a result, the associated pointer travels on a calibrated scale to display the temperature.




Spiral bimetallic thermometer temperature range:
It can be used to measure the temperature from 30°C to 550°C.
Applications of Spiral Bimetallic Thermometer:
Following are the application of of Spiral Bimetallic Thermometer.
- In homes and workplaces to measure the temperature of the surrounding air (ambient air temperature).
- In commerce and for industrial applications.
Advantage of Helical Bimetallic thermometers and Spiral Bimetallic thermometers:
Helical Bimetallic thermometers and Spiral Bimetallic thermometers have the following advantages over plain thermometers that make them appropriate for use in industrial applications:
- The pointer deflects more.
- High senstivity
Due to the short length of the bimetallic strip utilised, the deflection of the pointer in the case of the plain bimetallic thermometer is very minimal and constrained. This is due to the fact that the deflection of the free end is precisely proportional to the square of the metal strip’s length. Bimetallic strip length must be significantly expanded in order to have more deflection and to measure high temperatures. Such a longer simple bimetallic thermometer would take up more room and be impractical to use. Bimetallic thermometers of the helix or spiral type are able to solve this challenge.
The length of the strip can be extended to increase sensitivity. In order to make the instrument smaller and more portable, if the length of strip needed is too long, it can be bent into a spiral or helix. Due to this configuration, a very long strip can fit into a very tiny area.
Disadvantages of Bimetallic Thermometers:
Disadvantages of Bimetallic thermometer are as below.
- Bimetallic thermometers are unable to measure temperatures that are changing quickly. As a result, it is not advised to use them for temperature measurements that change quickly.
- Materials used in bimetallic thermometers may experience long-term distortion or deformation, which could prevent them from returning to their original dimensions. Temperature measurements and indications could be wrong in such circumstances.
- Slow response time.
Advantages of Bimetallic Thermometers:
Advantages of Bimetallic thermometer are as below.
- Low price.
- Simple to install and keep up.
- Excellent precision up to +/-0.5%.
- Wide temperatures range.
- The ability to survive being heated up to a temperature that is 1.5 times greater than the one for which it was designed.
- Tough to break.
- Simple and little in size.
- Strong construction
Applications of Bimetallic Thermometers:
The main Application of bimetallic thermometer are
- In Thermostats that are ON or OFF types
- In the Systems that regulate temperature.
- In Control switches for home appliances like refrigerators, electric irons, and ovens.
- In Industrial uses such refineries and oil burners, etc.
- In lamp flashes.
- In time delay Circuits.
How to select a Bimetallic Thermometer?
When selecting a bimetallic thermometer, keep the following things in mind.
- The nature of the connection
- Temperature range.
- Dial or case size.
- Stem or capillary length.
- The thermometer may suffer from improper application. Failure to do so could result in both a personal loss and a loss of property. When installing a thermometer, it’s crucial to pay attention to the area around it because that will affect the sort of thermometer we need to use.
- Potential, conduction, radiation, noise, response time, and grounding problems are some of the different faults that can happen when monitoring temperature.
Recommended Articles:-
What is Thermocouple and its Tpyes
What are the pressure sensing elements
What is Thermometer ? What are the types of Thermometer ?