Table of Contents
In the world of engineering and automation, actuators play a vital role in converting various types of energy into mechanical motion. Actuators are widely used in different industries and applications, offering precise and controlled movement. Among the various types of actuators, linear actuators and rotary actuators are commonly used. While they both serve the purpose of providing motion, there are significant differences between the two. This article aims to explore the dissimilarities between linear actuators and rotary actuators, highlighting their unique characteristics, applications, and advantages.
Definition of Linear Actuator
A linear actuator is a mechanical device capable of producing linear motion or movement in a straight line. It converts various types of energy, such as electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic, into linear motion. Linear actuators are widely used in applications that require controlled and precise movement in a linear direction.
Definition of Rotary Actuator
A rotary actuator, on the other hand, is a mechanical device that generates rotational motion. It converts energy into a rotary or circular motion, allowing objects or mechanisms to rotate around an axis. Rotary actuators find applications in scenarios where rotational movement is required.






Working Principle of Linear Actuator
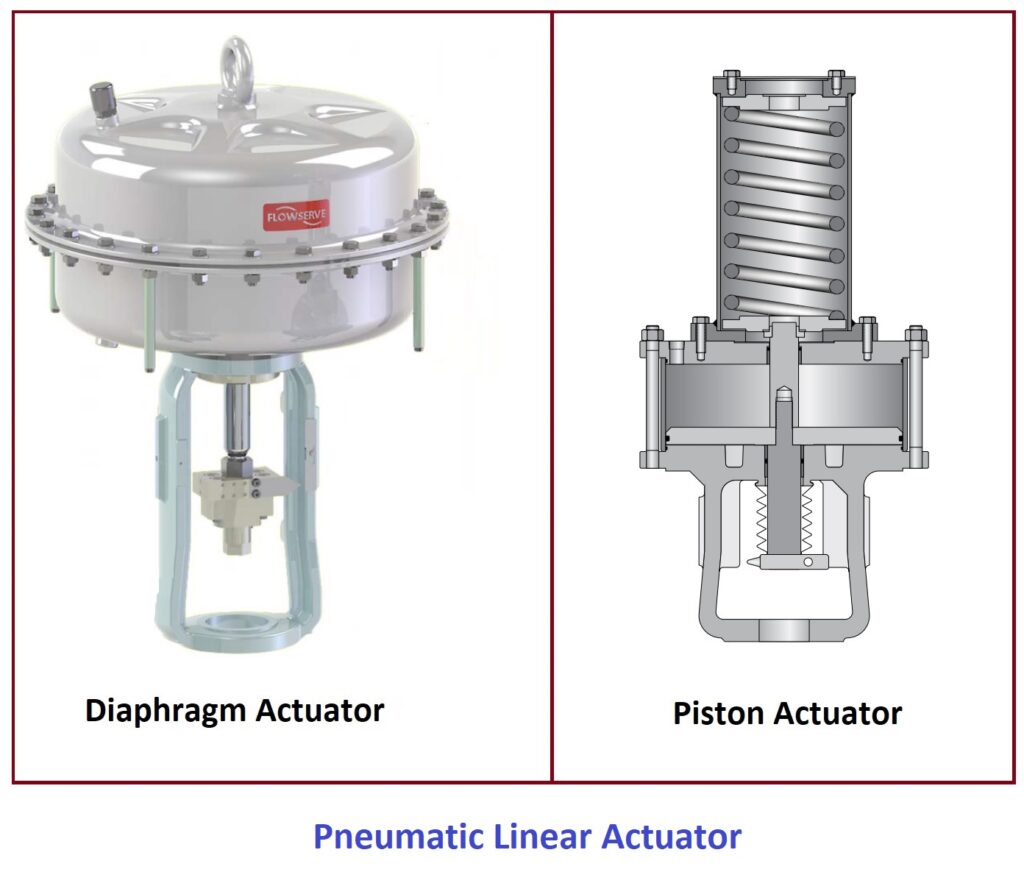
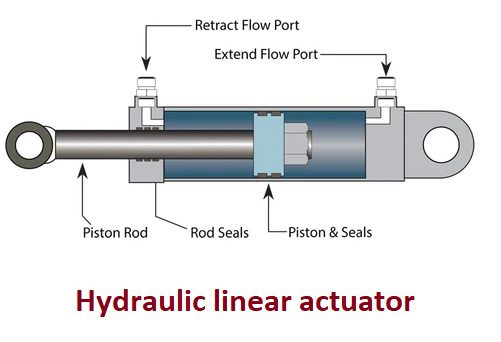
Linear actuators operate on different principles depending on their type. Electric linear actuators typically use a motor that drives a lead screw or a belt mechanism. When the motor rotates, the lead screw or belt translates the rotational motion into linear motion, causing the actuator to extend or retract. Hydraulic linear actuators use hydraulic pressure to move a piston or rod, creating linear movement. Pneumatic linear actuators, on the other hand, use compressed air to generate linear motion through the expansion and contraction of a piston or diaphragm.
Working Principle of Rotary Actuator
Similar to linear actuators, rotary actuators also have various working principles. Electric rotary actuators utilize an electric motor to drive a gear or a shaft, resulting in rotational movement. Hydraulic rotary actuators use hydraulic pressure to generate torque and rotation. Pneumatic rotary actuators employ compressed air to create rotational motion by expanding and contracting chambers or pistons.
Types of Linear Actuators
Linear actuators can be categorized into different types based on their mode of operation and the energy source they utilize. Some common types of linear actuators include:
- Electric Linear Actuators: These actuators use an electric motor to produce linear motion. They are widely used in applications such as robotics, industrial automation, and home automation systems.





- Hydraulic Linear Actuators: Hydraulic linear actuators rely on hydraulic pressure to create linear motion. They are often found in heavy-duty machinery and applications that require high force and precision.




- Pneumatic Linear Actuators: Pneumatic linear actuators use compressed air to generate linear motion. They are commonly used in industries such as packaging, automotive, and aerospace.






Types of Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators, too, come in different types depending on their energy source and design. Some common types of rotary actuators include:
- Electric Rotary Actuators: Electric rotary actuators use an electric motor to drive rotational movement. They find applications in robotics, CNC machines, and various automated systems.





- Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: Hydraulic rotary actuators utilize hydraulic pressure to generate torque and rotational motion. They are often employed in heavy machinery and industrial applications.





- Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Pneumatic rotary actuators rely on compressed air to create rotary motion. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, processing, and material handling.






Applications of Linear Actuators
Linear actuators are versatile devices with numerous applications across various industries. Some common applications include:
- Electric adjustable beds and chairs
- Solar panel tracking systems
- Medical equipment, such as hospital beds and patient lifts
- Automotive industry, for opening and closing doors or hoods
- Industrial automation and robotics
- Home automation systems, like smart curtains or windows
Applications of Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators also find extensive usage in a wide range of applications. Some notable examples include:
- Robotic arms and manipulators
- Conveyor systems
- Valve control in industrial processes
- Aerospace and aviation industry, for controlling aircraft surfaces
- Automated manufacturing equipment
- Printing presses and paper processing machines
Advantages of Linear Actuators
Linear actuators offer several advantages that make them suitable for specific applications. Some key advantages include:
- Precise and controlled linear motion
- Compact and lightweight design
- High force and load capacity
- Easy integration into existing systems
- Wide range of available options and customization
Advantages of Rotary Actuators
Rotary actuators also possess unique advantages that make them favorable for certain applications. Some notable advantages include:
- Smooth and continuous rotational motion
- High torque output
- Capability to rotate heavy loads
- Simple installation and maintenance
- Versatility in mounting options
Key Differences Between Linear Actuator and Rotary Actuator
While both linear actuators and rotary actuators serve the purpose of providing motion, they differ significantly in terms of their motion type, applications, and design. Here are the key differences between the two:
- Motion Type: Linear actuators produce linear or straight-line motion, while rotary actuators generate rotational or circular motion.
- Applications: Linear actuators are commonly used in applications that require linear movement, such as adjustable furniture, robotics, and automation systems. Rotary actuators, on the other hand, find applications in scenarios that involve rotational movement, such as robotic arms, conveyors, and industrial processes.
- Design: Linear actuators are typically elongated devices that extend and retract in a straight line. Rotary actuators, on the other hand, are compact and designed to rotate around an axis.
- Force and Torque: Linear actuators excel in providing high force and load capacity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Rotary actuators, on the other hand, offer high torque output, allowing them to rotate heavy loads.
- Mounting Options: Linear actuators can be mounted in various orientations, such as vertically or horizontally, depending on the application. Rotary actuators offer flexibility in terms of mounting options, allowing them to be integrated into different systems easily.
In conclusion, while both linear actuators and rotary actuators serve distinct purposes, their differences lie in the type of motion they produce, their applications, and their design features. Choosing the appropriate actuator depends on the specific requirements of the application at hand.
FAQs
FAQ 1: What is the main difference between linear and rotary actuators?
- The main difference lies in the type of motion they generate. Linear actuators produce linear or straight-line motion, while rotary actuators generate rotational or circular motion.
FAQ 2: Can a linear actuator be converted into a rotary actuator?
- No, a linear actuator cannot be converted into a rotary actuator as they operate on different principles and are designed for specific types of motion.
FAQ 3: Which actuator is more suitable for heavy-duty applications?
- Linear actuators are generally more suitable for heavy-duty applications as they offer high force and load capacity.
FAQ 4: Are linear actuators more expensive than rotary actuators?
- The cost of actuators can vary depending on factors such as size, force capacity, and quality. However, in general, linear actuators tend to be more expensive than rotary actuators due to their complex design and functionality.
FAQ 5: Can linear and rotary actuators be used together in a single system?
- Yes, linear and rotary actuators can be used together in a single system to achieve complex motions that involve both linear and rotational movement. This combination can provide enhanced functionality and versatility in certain applications.
Read Also
- Troubleshooting common Control Valve Problems
- How to Solve On-Off Valve Problems ?
- Control valve Leakage Problem
- Pressure Control Valve
- Control Valve Positioner