Table of Contents
Infra red gas analyzer work :-
An infra red gas analyzer measures trace gases by determining the absorption of an emitted infrared light source through a certain air sample. Trace gases found in the Earth’s atmosphere get excited under specific wavelengths found in the infrared range. The concept behind the technology can be understood as testing how much of the light is absorbed by the air. Different molecules in the air absorb different frequencies of light. Air with lots of a certain gas will absorb more of a certain frequency, allowing the sensor to report a high concentration of the corresponding molecule.
IR Gas analyzer can be of two types
- Non-Dispersive Infra Red Analyzer
- Dispersive Infra Red Analyzer
1. Non-Dispersive Infra Red Analyzer
- A non dispersive infrared sensor (or NDIR) sensor is a simple spectroscopic device often used as gas detector.
- It is called non dispersive because wavelength which passes through the sampling chamber is not pre-filtered instead a filter is used before the detector.
- NDIR analyzer is designed to continuously monitor the concentration of a particular infrared absorbing component of a gas in a flowing gaseous mixture.
- The concentration of a gas is displayed as a percent of full scale according to output signal of 0-5 VDC or 4-20 MA.
- CO2, CO, CH4, SO2, NH3 can be measured.
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF NDIR DETECTION SYSTEM
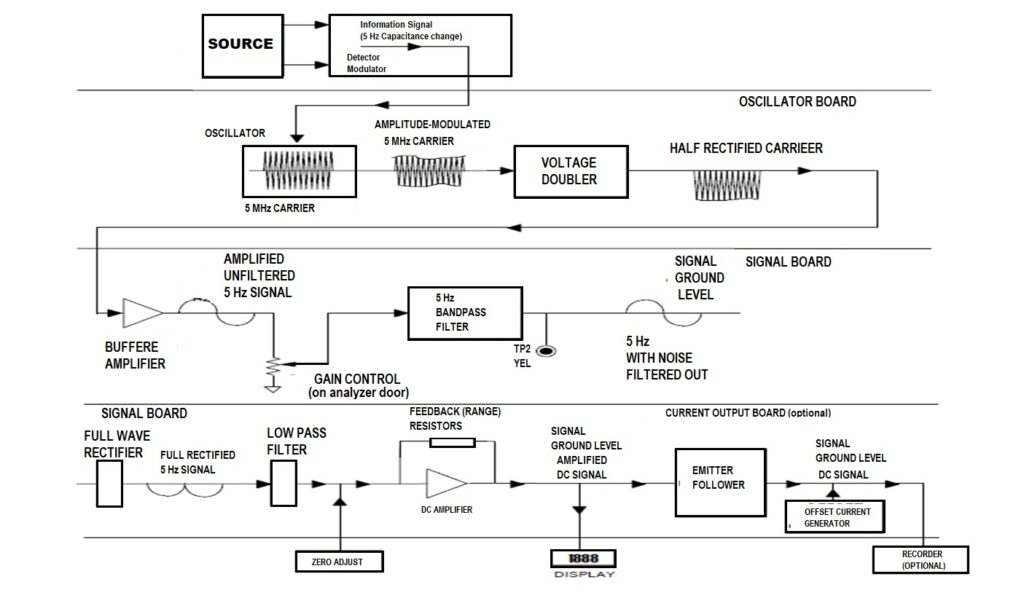
As shown in Fig, infrared radiation is produced from two separate energy sources.

- This radiation is interrupted by a chopper at 5 Hz.
- The two equal beams are then directed through two parallel optical cell/chamber( sample cell and reference cell).
- A portion of the infrared radiation is absorbed by the sample gas, the quantity of which is proportional to the sample gas concentration.
- The detector has an optical filter in front of it that eliminates all light except the wavelength that the selected gas molecules can absorb. Ideally other gas molecules do not absorb light at this wavelength, and do not affect the amount of light reaching the detector to compensate for interfering components.
DETECTOR PART
- The signal from the two cells after the filter then goes to the two different chambers of the detector unit.
- The diaphragm is distended depending up to the difference between the two signals which in turn is proportional to the concentration of the sample gas.
- This value of capacitance is directly proportional to the difference between the reference and sample cells signals.
- The capacitance is used to modulate the amplitude of a radio frequency voltage, which is then demodulated into a resulting DC voltage signal.
- The output signal is proportional to the component concentration; it is amplified and sent to the digital display.
- When chopper blocks the radiation, pressure in both parts of detector is same and diaphragm remains in neutral position.
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF OUTPUT SIGNAL




Correlation between Gases (molecules) and electromagnetic radiation





The gas will absorb the IR energy of this wavelength and transmit IR energy of other wavelengths.
Ex. – Absorption band for CO is between 4.5 and 5 microns. So energy absorbed at this wavelength is an indication of concentration of CO in exhaust gas.
2. Dispersive Infra Red Analyzer
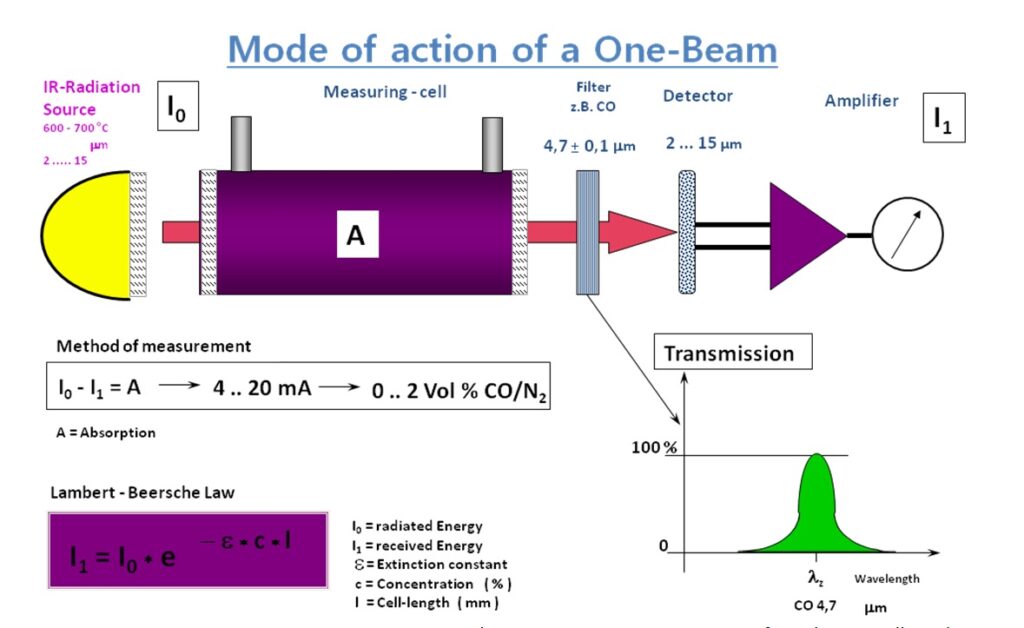




The main components are an infrared source (lamp), a sample chamber or light tube, a wavelength sample chamber, and gas concentration is measured electro-optically by its absorption of a specific wavelength in the infrared (IR). The IR light is directed through the sample chamber towards the detector. In parallel there is another chamber with an enclosed reference gas, typically nitrogen. The detector has an optical filter in front of it that eliminates all light except the wavelength that the selected gas molecules can absorb. Ideally other gas molecules do not absorb light at this wavelength, and do not affect the amount of light reaching the detector to compensate for interfering components. For instance, CO2 and H2O often initiate cross sensitivity in the infrared spectrum. As many measurements in the IR area are cross sensitive to H2O it is difficult to analyze for instance SO2 and NO2 in low concentrations using the infrared light principle.
The IR signal from the source is usually chopped or modulated so that thermal background signals can be offset from the desired signal. A non-dispersive infrared sensor (or NDIR) sensor is a simple spectroscopic device often used as gas detector. It is called non-dispersive because wavelength which passes through the sampling chamber is not pre-filtered instead a filter is used before the detector.
Read Also:-
How Infra Red Gas analyzer Work
Related Search:-